Extended Data Figure 1. Molecular and structural characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD sortase A conjugated nanoparticle.
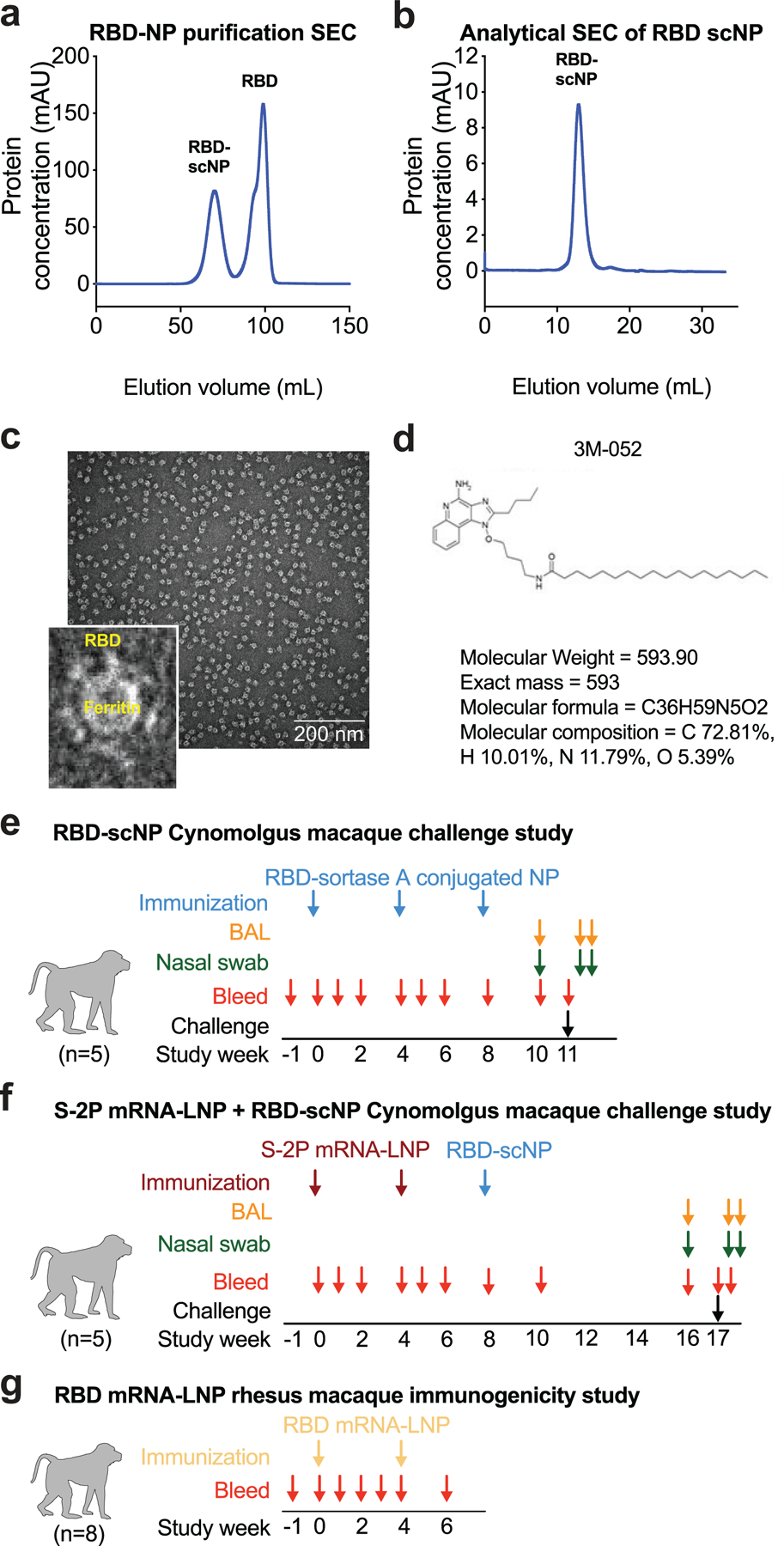
a Size exclusion chromatography of RBD and ferritin sortase conjugation. The first peak shows conjugated protein. The second peak contains unconjugated RBD.
b Analytical size exclusion trace shows a homogenous nanoparticle preparation.
c Negative stain electron microscopy image of RBD-scNPs on a carbon grid. Inset shows a zoomed image of RBD-scNP. The zoomed image shows RBD molecules arrayed around the outside of the ferritin nanoparticle. A representative image from the 31 images taken of the micrograph to visualize 13,827 total particles is shown.
d Chemical structure of toll-like receptor 7 and 8 agonist 3M-052. Alum formulation of 3M-052 was used to adjuvant RBD-scNP immunization.
e RBD-scNP immunization regimen used for vaccination of cynomolgus macaques (N=5). Blue arrows indicate timepoints for intramuscular immunizations with RBD-scNP (100 µg) adjuvanted with 3M-052 (5 µg 3M-052 plus 500 µg Alum). Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL, orange arrows) and nasal swab (green arrows) fluids were collected 7 days before, 2 days after, and 4 days after intratracheal/intranasal SARS-CoV-2 challenge (black arrow).
f Transmembrane, diproline-stabilized spike (S-2P) mRNA-LNP prime, RBD-scNP boost vaccination of cynomolgus macaques (N=5). Maroon arrows indicate timepoints for S-2P mRNA-LNP immunization (50 µg mRNA dose). Blue arrows are the same as in a. Macaques were challenged 9 weeks after RBD-scNP boost (week 17 of the study). BAL and nasal swab fluids were collected as in a. Macaques were challenged at week 17 (black arrow).
g Monomeric RBD mRNA-LNP immunization of rhesus macaques (N=8). Tan arrows indicate timepoints for RBD mRNA-LNP immunization (50 µg mRNA dose). Blood was collected throughout each study as shown by red arrows in all panels.
