Extended Data Figure 5. Cross-reactive plasma antibody responses elicited by RBD-NP immunization in macaques.
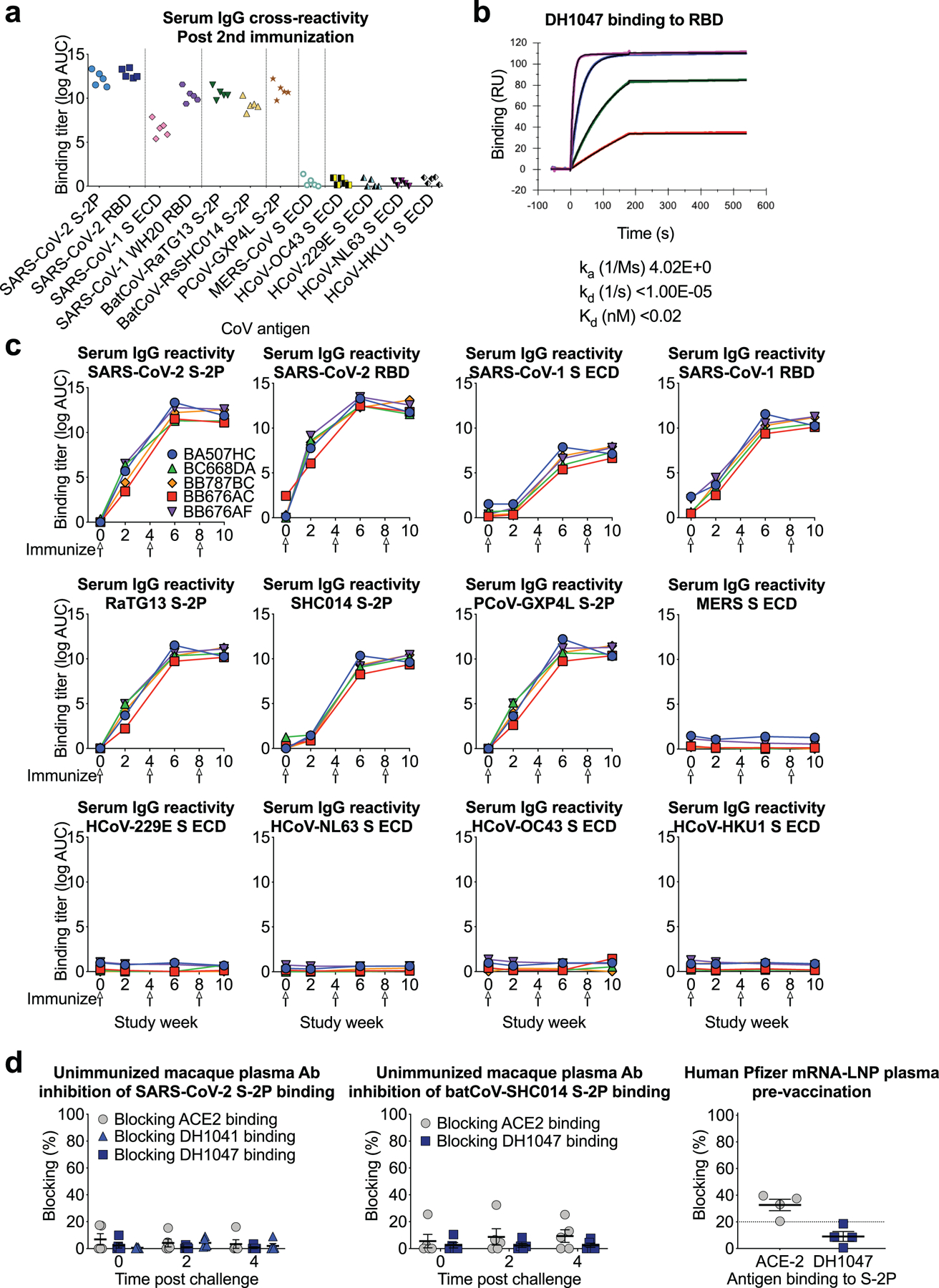
a Plasma IgG from macaques immunized twice with RBD-scNP binds to Spike from human, bat, and pangolin SARS-related coronavirus Spike (S) in ELISA, but not endemic human coronaviruses or MERS-CoV. ECD, ectodomain.
b Determination of DH1047 antigen binding fragment (Fab) binding kinetics to RBD monomer by surface plasmon resonance. Each curve shows a different concentration of DH1047 Fab. Binding kinetics are shown to the right from a 1:1 model fit.
c Time course of vaccinated macaque plasma IgG binding to human, bat, and pangolin coronavirus S protein by ELISA. Each curve indicates the binding titer for an individual macaque. Arrows indicate immunization time points.
d Unimmunized macaque plasma antibody blocking of SARS-CoV-2 S-2P (left) and batCoV-SHC014 (middle) binding to ACE2-Fc, RBD neutralizing antibody DH1041, and RBD cross-nAbDH1047. (Right) Blocking activity in the serum of humans immunized with Pfizer S-2P mRNA-LNP vaccine (N=4). Each symbol represents an individual human or macaque. Bars indicate group mean±s.e.m.
