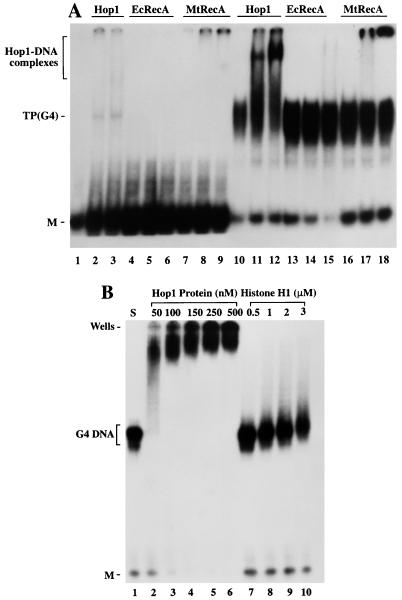
FIG. 5.
RecA proteins and histone H1 fail to form G4 DNA complexes that are stable to electrophoresis. (A) Assays with Hop1 protein in comparison with the RecA proteins. Reactions were performed in assay buffer (20 μl) containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 pmol of 32P-labeled TP oligonucleotide (lanes 1 to 9) or its G-quartet structure, TP G4 DNA (lanes 10 to 18), plus the proteins indicated above each lane. Lanes 1 and 10 are controls lacking any added protein. As a positive control, Hop1 protein was substituted at a concentration of 50 nM (lanes 2 and 11) or 100 nM (lanes 3 and 12) in the presence of 0.1 mM ZnCl2. Identical G4 DNA samples were incubated with RecA protein from E. coli (EcRecA) at a concentration of 100 nM (lanes 4 and 13), 250 nM (lanes 5 and 14), or 500 nM (lanes 6 and 15) and with that from M. tuberculosis (mtRecA) at 100 nM (lanes 7 and 16), 250 nM (lanes 8 and 17), or 500 nM (lanes 9 and 18) in the presence of 1.5 mM ATP and 2 mM MgCl2. (B) Histone H1 fails to bind G4 DNA under these conditions. Reactions were carried out with TP G4 DNA with Hop1 or histone H1 at concentrations indicated above each lane. Samples were separated on a 6% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by autoradiography as described in Materials and Methods. M, unfolded TP monomer.