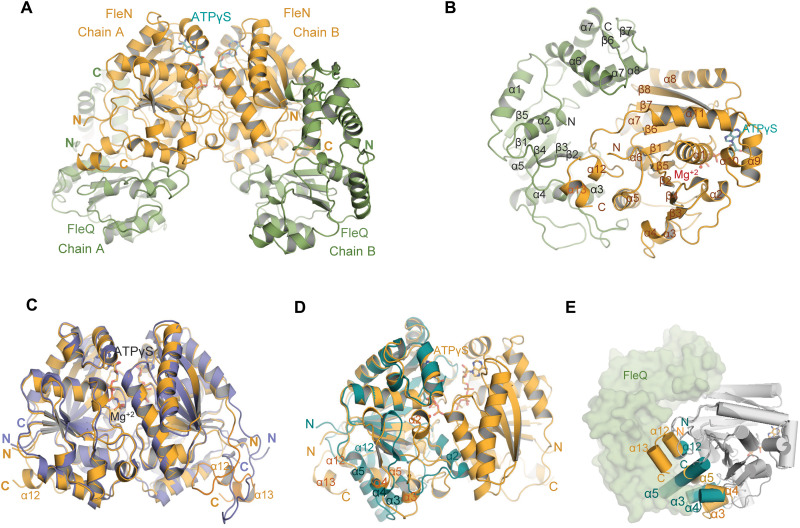
Fig. 2. Structure of FleN-ATPγS-FleQAAA+ complex.
(A) FleN-ATPγS-FleQAAA+ structure showing the FleN dimer in bright orange in complex with ATPγS in cyan, interacting with FleQAAA+ domains colored green forming a heterotetrameric complex. (B) Half of the complex containing one monomer of FleN and one molecule of FleQAAA+. All the secondary structure elements are labeled. ATPγS and Mg+2 are shown in cyan stick and red sphere, respectively. (C) Superimposition of dimeric FleN from AMP-PNP–bound structure [slate, Protein Data Bank (PDB): 5J1J] and FleQ-bound structure (bright orange) from the FleN-ATPγS-FleQAAA+ complex depicts structural changes at the C-terminal end. (D) Superimposition of the FleN dimer from the FleN-ATPγS-FleQAAA+ complex structure (bright orange) onto the Apo-FleN monomer (deep teal, PDB: 5JVF). The conformational changes in the helices are depicted. (E) Superimposition of FleN-Apo monomer (light gray with α3, α4, α5 and α12 in deep teal, PDB: 5JVF) onto FleN bound to ATPγS-FleQAAA+ (dark gray with α3, α4, α5, α12, and α13 in orange) showing steric clash between the monomeric FleN (deep teal) and FleQ (green) shown in surface representation. Helices are depicted as cylinders.