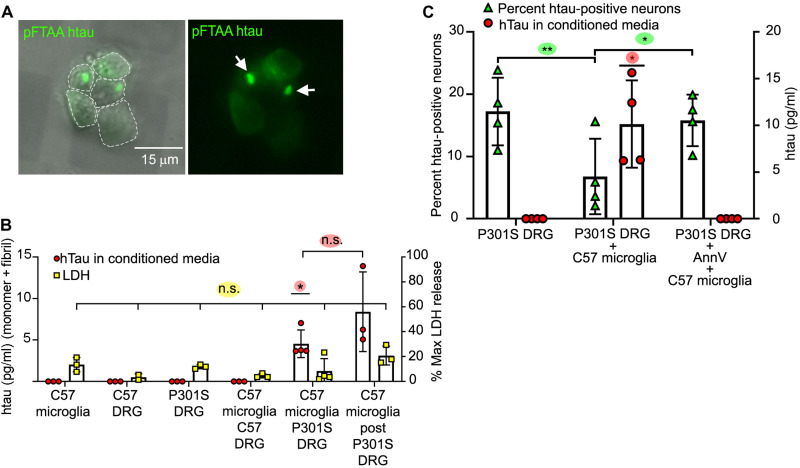
Fig. 1. Microglia that have phagocytosed P301S DRGn containing tau aggregates release htau into the CM.
(A) Tau aggregates in 5M P301S DRGn prelabeled with pFTAA are transferred to microglia after phagocytosis. Microglia were purified after 4 days of coculture, replated, and imaged live. Left: Fluorescence and phase. Right: Fluorescence only. Arrows, pFTAA-positive tau foci. (B) htau is only released into the CM when 5M P301S DRGn and microglia are cocultured. Human transgenic tau was detected specifically by ELISA after 4 days (P = 0.012, versus all monocultures and coculture of microglia with 5M C57 neurons, one-sample t test). Tau is released over a further 4 days by microglia reisolated from 5M P301S DRGn cocultures (post) (P = 0.185 versus original coculture CM, unpaired t test). No tau is detected in CM from monocultures of 5M P301S or C57 DRGn or C57 microglia or from 5M C57 DRGn-microglia cocultures. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity is not significantly different across all conditions, indicating that released tau is not due to lysed cells (P = 0.069, one-way ANOVA). N = 3 to 4 independent experiments, means ± SD. (C) Release of tau requires phagocytosis by microglia. The number of htau-positive 5M P301S DRGn (% HT7/βIII-tubulin) is reduced after coculture with C57 microglia (green triangles, P = 0.0048, repeated-measures ANOVA), commensurate with an increase in tau in the CM (red circles, P = 0.0225, one-sample t test). Blocking phagocytosis by masking PtdSer with AnnV prevents neuronal loss (green triangles, n.s. versus P301S DRG, P = 0.0309 versus C57 microglia, repeated-measures ANOVA). AnnV also prevents the release of tau into the CM (red circles, n.s. versus P301S DRG). N = 4 independent experiments, means ± SD.