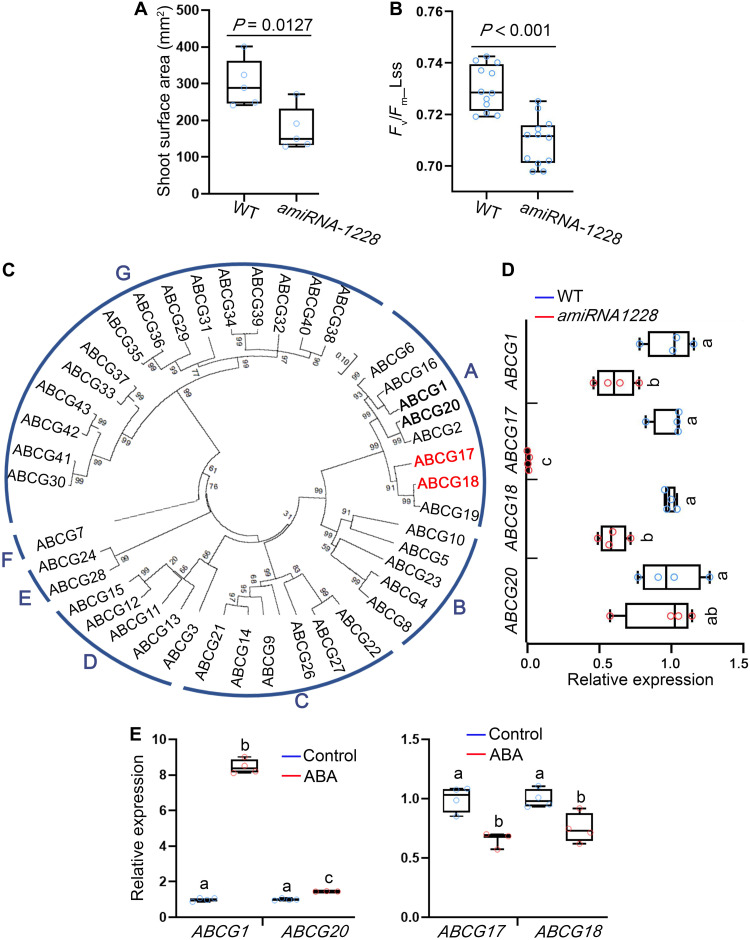
Fig. 1. Reduced expression of several class A ABCG members results in moderate shoot growth and decreased photosynthesis rate.
(A) Shoot surface area of 18-day-old WT and amiRNA-1228. Shown are averages (±SD), n = 5; P value indicates significant differences, Student’s t test. (B) Fv/Fm_Lss, indicating photosystem II quantum yield of light-adapted samples at steady state, measured for 18-day-old WT and amiRNA-1228. Shown are averages (±SD), n = 12; P < 0.001 (P = 1.15208 × 10−5) indicates significant differences, Student’s t test. (C) Phylogenetic tree of Arabidopsis ABCG family based on amino acid sequences. Red and bold fonts indicate proteins coded by putative amiRNA-1228 target genes. (D) Relative expression of the indicated ABCG amiRNA-1228–targeted genes in 12-day-old WT and amiRNA-1228 seedlings, quantified by qRT-PCR. Shown are averages (±SD), n = 4; different letters represent significant differences, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Student’s t test (P < 0.05). (E) Relative expression, quantified by qRT-PCR, of the indicated ABCG amiRNA-1228–targeted genes in response to ABA treatment (5 μM ABA for 3 hours) in 7-day-old seedlings. Shown are averages (±SD), n = 4; different letters represent significant differences, one-way ANOVA with Student’s t test (P < 0.05).