Figure 1.
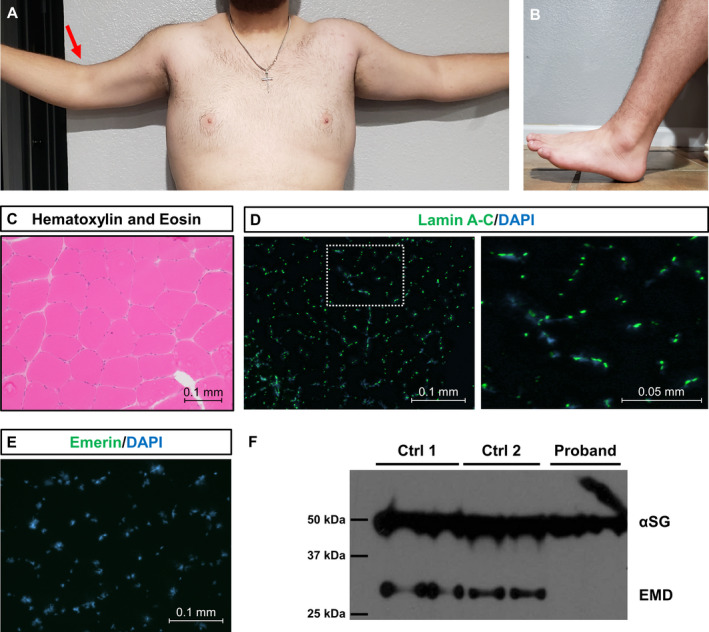
Clinicopathological features of proband with X‐linked Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (A) Photograph of proband’s fully extended arms demonstrating limited active range of motion due to elbow contractures (right greater than left, red arrow). (B) Photograph of proband’s fully dorsiflexed foot demonstrating limited active range of motion due to ankle contractures. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of left vastus lateralis muscle biopsy taken at 11 years old. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of lamin A‐C in the proband. Lamin A‐C is a nuclear protein involved in autosomal dominant Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 1 (MIM #310300). Lamin A‐C (green) is widely expressed and co‐localizes with the nuclear stain DAPI (blue). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of emerin in the proband. Note the absence of emerin staining (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (F) Western blot of muscle biopsy protein lysates from proband and two control patients using antibodies for alpha‐sarcoglycan (αSG) and emerin (EMD). All samples were run in duplicate. Molecular weights are provided in kilodaltons (kDa). A 50 kDa band is seen in all samples corresponding to αSG. A 34 kDa band corresponding to EMD can be seen in the control samples but not in the proband.
