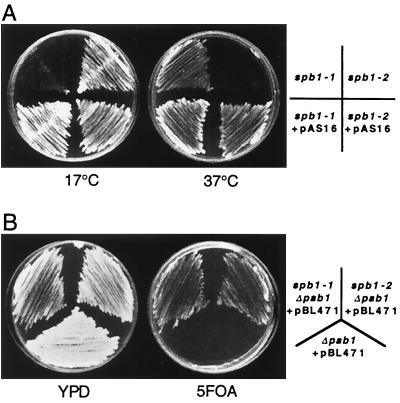
FIG. 1.
Strains spb1-1 and spb1-2 are complemented by the wild-type SPB1 gene, and both behave as suppressors of pab1Δ. (A) The wild-type SPB1 gene can restore normal growth of both spb1-1 and spb1-2. Strains spb1-1 (YAS 151), spb1-2 (JR4710), or these strains transformed by the plasmid pAS16 that contains the wild-type SPB1 gene (YBL4383 and YBL4384, respectively) were streaked onto yeast-peptone-dextrose (YPD) plates and grown at 17°C (for 7 days) or at 37°C (for 3 days). (B) Double mutants spb1-1 pab1Δ (YBL4459) and spb1-2 pab1Δ (YBL4258) were streaked onto a YPD plate, along with a single pab1Δ strain as a control. These three strains harbor the plasmid pBL471 that bears a wild-type PAB1 gene that complements the absence of PAB1 on their chromosome and a URA3 gene as a marker. When streaked onto 5-FOA-containing plates, the pab1Δ strain is unable to grow due to its inability to lose the PAB1 gene (plasmid pBL471 containing the URA3 gene), while both spb1-1 and spb1-2 are able to lose this plasmid and thus to grow on these plates.