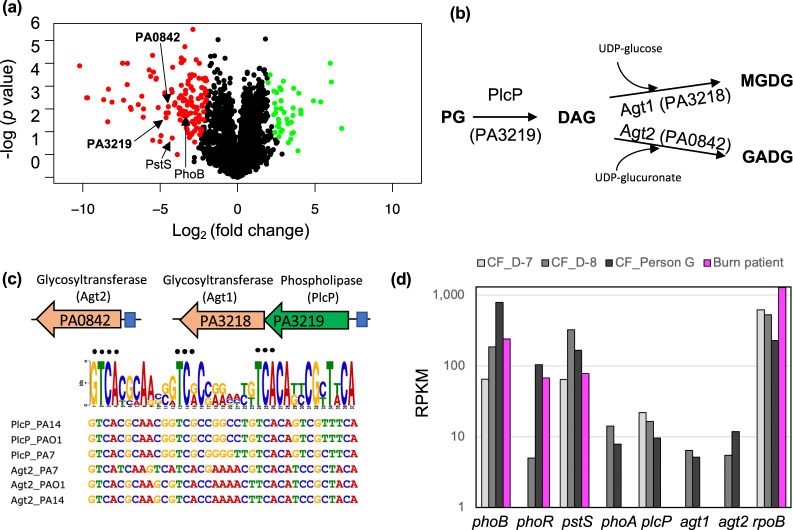
Fig. 2. Comparative multi-omic analyses for the identification of the PlcP-Agt pathway responsible for glycolipid formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1.
a Volcano plot depicting differentially expressed proteins when comparing Pi-replete and Pi-deplete conditions. Significantly upregulated proteins when under Pi stress are shown in red (left), and those that are significantly upregulated when Pi is sufficient are in green (right). Significance was accepted when the false discovery rate (FDR) was <0.05, and a fold change ≥2. b The proposed pathway for lipid remodelling through the PlcP-Agt pathway. PlcP degrades membrane phospholipids such as PG, to generate diacylglycerol (DAG) intermediates for the formation of MGDG and GADG through the activity of glycosyltransferases, using either UDP-glucose or UDP-glucuronate as the co-substrate [41]. c Genomic organisation of predicted lipid remodelling genes in P. aeruginosa. Glycosyltransferases (orange) PA3218 (Agt1) and PA0842 (Agt2) are predicted to be involved in glycolipid synthesis. PA3219 is predicted to be PlcP in P. aeruginosa. Predicted Pho box sequences in the promoter regions (represented in blue boxes) of each glycosyltransferase operon from P. aeruginosa strains representing the PAO1 clade, the PA7 clade and the PA14 clade are shown. The black dots represent residues which are conserved in the Pho box consensus CTGTCATNNNNCTGTCAT [42]. d Metatranscriptomic analysis of PlcP-Agt lipid remodelling genes in sputum samples from a cystic fibrosis patient 7-days (CF_D-7) and 8-days (CF_D-8) before death [26] and a Danish CF patient (CF_Person G) [27] as well as a wound sample from a burns patient from the USA (Burn patient) [27]. Relative abundance is expressed as RPKM (reads per kilobase of transcript, per million mapped reads). PhoA (PA3296) encodes an alkaline phosphatase [38]. The list of RPKM abundance of individual genes of P. aeruginosa PAO1 is shown in Table S4.