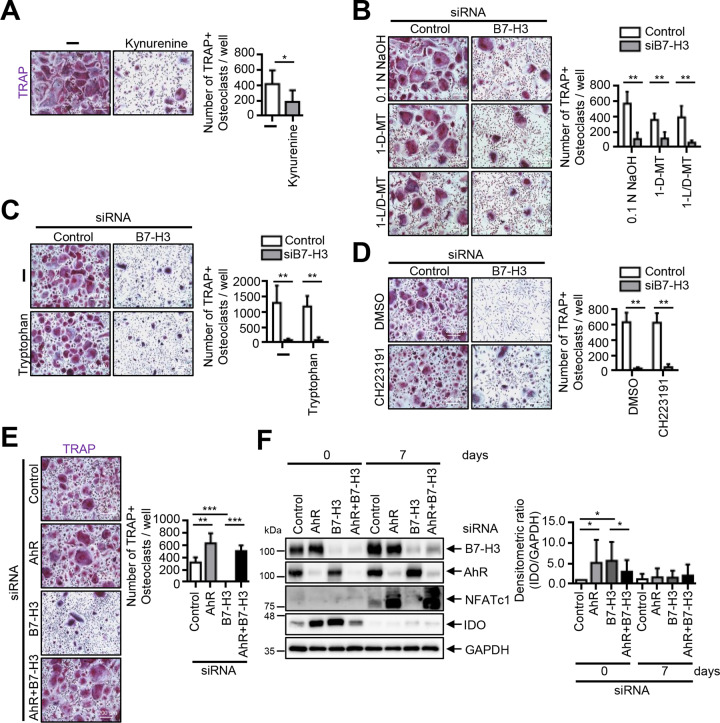
Fig. 7. The inhibition of osteoclastogenesis is independent of the IDO/tryptophan pathway in B7–H3-deficient OCPs.
A Monocytes were cultured with M-CSF (20 ng/ml) for two days, then M-CSF (20 ng/ml) and RANKL (40 ng/ml) were added for an additional six days in the presence of kynurenine (100 μM) or DMSO. B M-CSF (40 ng/ml) was added to monocyte culture for three days. OCPs that were transiently transfected with B7–H3-specific siRNA or control siRNA (20 nM) were induced to differentiate using M-CSF (40 ng/ml) and RANKL (80 ng/ml) for seven days with coadministration of 1-D-MT (200 μM), 1-L/D-MT (200 μM), or 0.1 N NaOH (control). C The experiment in (B) was conducted, except with coadministration of tryptophan (1 mM) or distilled water (control). D The experiment in (B) was conducted, except with coadministration of CH223191 (5 μM) or DMSO (control). E The OCPs that were transiently transfected with B7–H3-specific siRNA (20 nM), AhR-specific siRNA (40 nM), control siRNA (60 nM), or both B7–H3- and AhR-specific siRNA were induced to differentiate using M-CSF (40 ng/ml) and RANKL (80 ng/ml) for seven days. F Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with B7–H3, AhR, NFATc1, and IDO Abs. The bar graphs show the densitometry analyses of the gels depicted relative to the internal control. (A, B, C, D, E) TRAP staining was performed and the number of TRAP-positive multinucleated cells per well were counted as osteoclasts (scale bar, 200 μm).