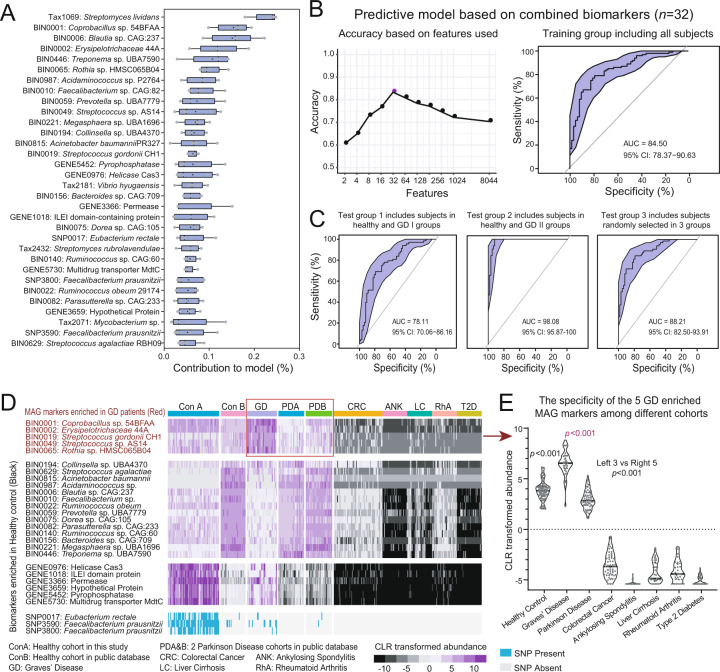
Fig. 4. Identification of GD-associated biomarkers using a machine learning approach and the multi-cohort analysis reveals gut microbiome biomarkers that are specific to GD.
A The importance of the biomarkers was ranked according to their contribution to the predictive model built by Random Forest. B, C The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under curve (AUC) both in the training and three test groups was calculated. D The heatmap shows the specificity of GD-associated MAG biomarkers to those commonly studied metabolic diseases: ankylosing spondylitis (ANK), liver cirrhosis (LC), colorectal cancer (CRC), Parkinson’s disease (PDA: a European cohort, PDB: a Chinese cohort), rheumatoid arthritis (RhA) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), as well as 2 healthy control cohorts (ConA and Con B). E The violin plot shows the quantitative difference in the total CLR-transformed abundance of the five marker MAGs across all the cohorts.