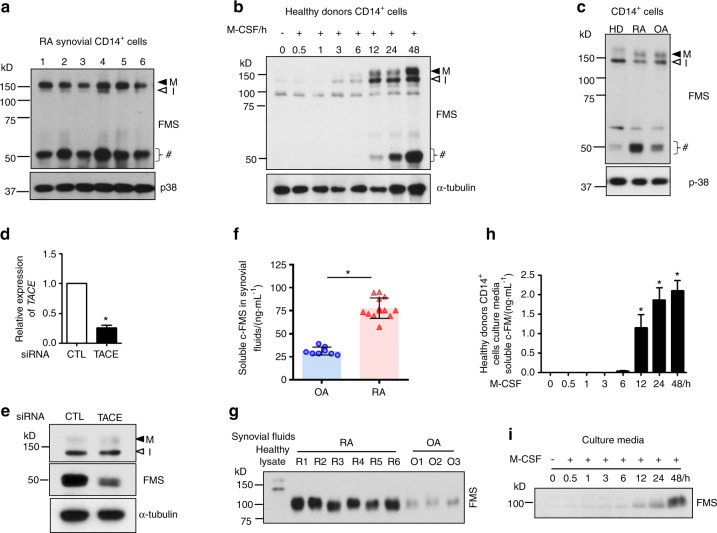
Fig. 1.
The detection of small fragments of c-FMS and soluble c-FMS. a Immunoblot analysis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial CD14+ cells with antibodies against the C-terminus of c-FMS. b Human CD14+ cells from healthy donors were cultured with M-CSF for the indicated times. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates with antibodies against the C-terminus of c-FMS. c Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates from CD14+ cells from healthy donors cultured with M-CSF for 1 day (HD) and synovial CD14+ cells from patients with RA or osteoarthritis (OA). d, e Human CD14+ cells were nucleofected with control (CTL) or TACE siRNAs and then cultured with M-CSF. d Knockdown (KD) efficiency. TACE mRNA was measured by qPCR and normalized to HPRT. e Immunoblot analysis of KD cells using an anti-c-FMS antibody. f, g Soluble c-FMS levels in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA, n = 13) and osteoarthritis (OA, n = 8) were measured by ELISA (f) and immunoblot analysis with antibodies against N-terminal c-FMS (g). h, i Human CD14+ cells were cultured with M-CSF. Soluble c-FMS in the culture media was measured by ELISA (h) and immunoblot analysis with anti-c-FMS antibodies (i). All data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 by unpaired t-test (d, f) or one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test (h). The data represent at least 3 independent donors. M; a mature c-FMS, I; an immature c-FMS, #; small fragments.