Fig. 7. Rondani’s wasp virus 1 (RoWV-1) is able to infect Drosophila melanogaster.
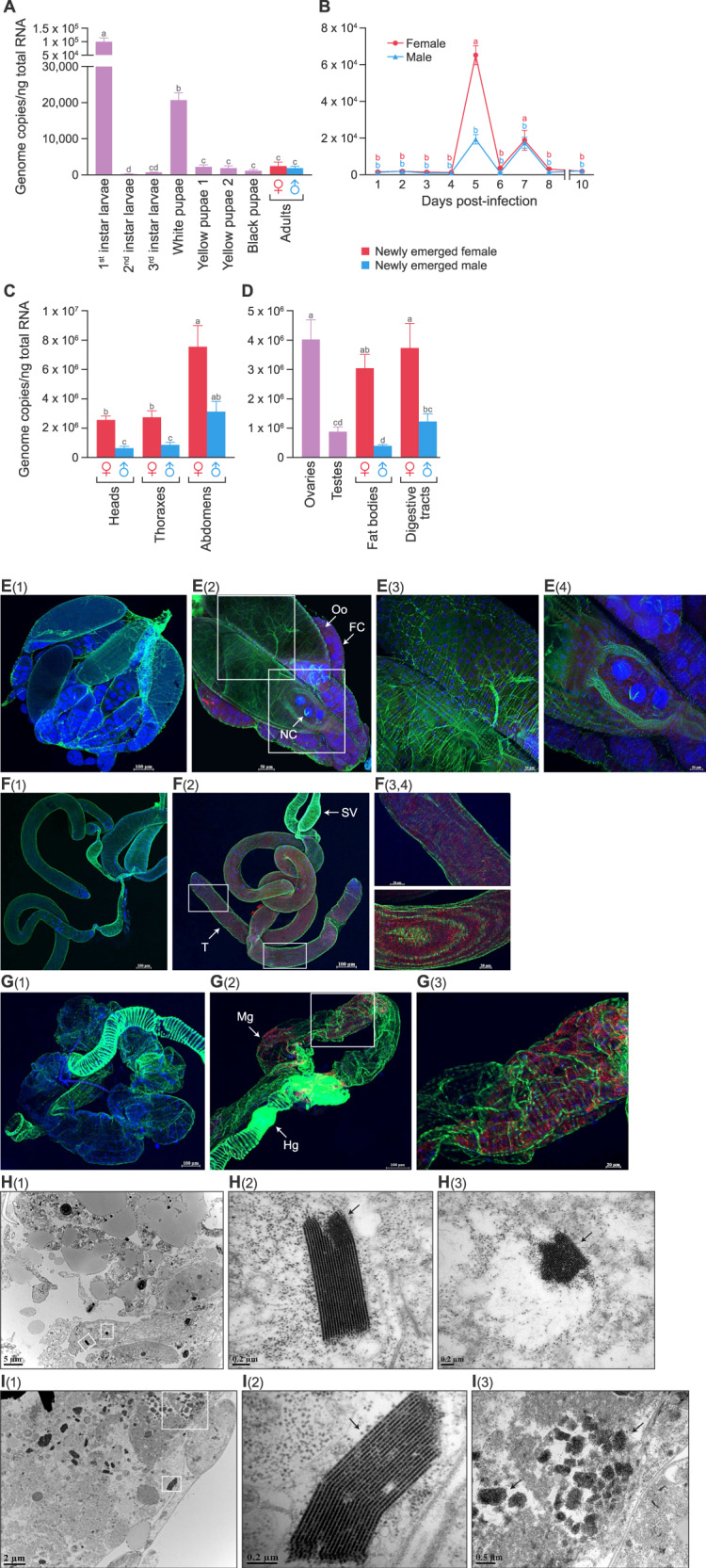
A RoWV-1 load in larvae, pupae, and adult D. melanogaster: yellow pupae 1, early-stage yellow pupae; yellow pupae 2, late-stage yellow pupae; adults refer to newly emerged male and female adults. B RoWV-1 load in adult flies at Day 1 through Day 10 after eclosion. C RoWV-1 load in D. melanogaster heads, thoraxes, and abdomens. D RoWV-1 load in adult D. melanogaster ovaries, testes, female digestive tracts, male digestive tracts, female fat bodies, and male fat bodies. Data represent means ± standard error of mean (SEM). Bars annotated with identical letters do not differ significantly (Tukey’s multiple comparison test). E Localization of RoWV-1 antigen (red) in D. melanogaster ovary. E(1), E(2) Adult fly’s ovary, stains were derived from dissected RoWV-1 (–) and RoWV-1 (+) D. melanogaster. E(3), E(4) The enlarged insets of the boxes in E(2): FC follicle cell, NC nurse cell, Oo oocyte. F Localization of RoWV-1 antigen (red) in D. melanogaster testis. F(1), F(2) Adult fly’s testis, stains were derived from dissected RoWV-1 (–) and RoWV-1 (+) D. melanogaster. F(3), F(4) The enlarged insets of the boxes in F(2). SV seminal vesicle, T testis. G Localization of RoWV-1 antigen (red) in D. melanogaster digestive tracts. G(1) Adult fly’s digestive tract, and G(2) adult fly’s digestive tract, stains were derived from dissected RoWV-1 (–) and RoWV-1 (+) D. melanogaster. G(3) The enlarged inset of the box in G(2): Hg hindgut, Mg midgut. F-actin was stained with phalloidin (green). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). H RoWV-1 particles observed in ovary (arrows) on transmission electron micrographs. H(2), H(3) The enlarged insets of the boxes in H(1). I RoWV-1 particles observed in testis (blue arrows) on transmission electron micrographs. I(2), I(3) The enlarged insets of the box in I(1). Multiple comparisons in one-way or two-way ANOVA are shown with lowercase letters, showing statistically significant difference at p < 0.05 for each treatment. A completely different letter means there is a significant difference between the two (e.g., a and b), but when the same letter is displayed, there is no significant difference between the two (e.g., a and a or a and ab).
