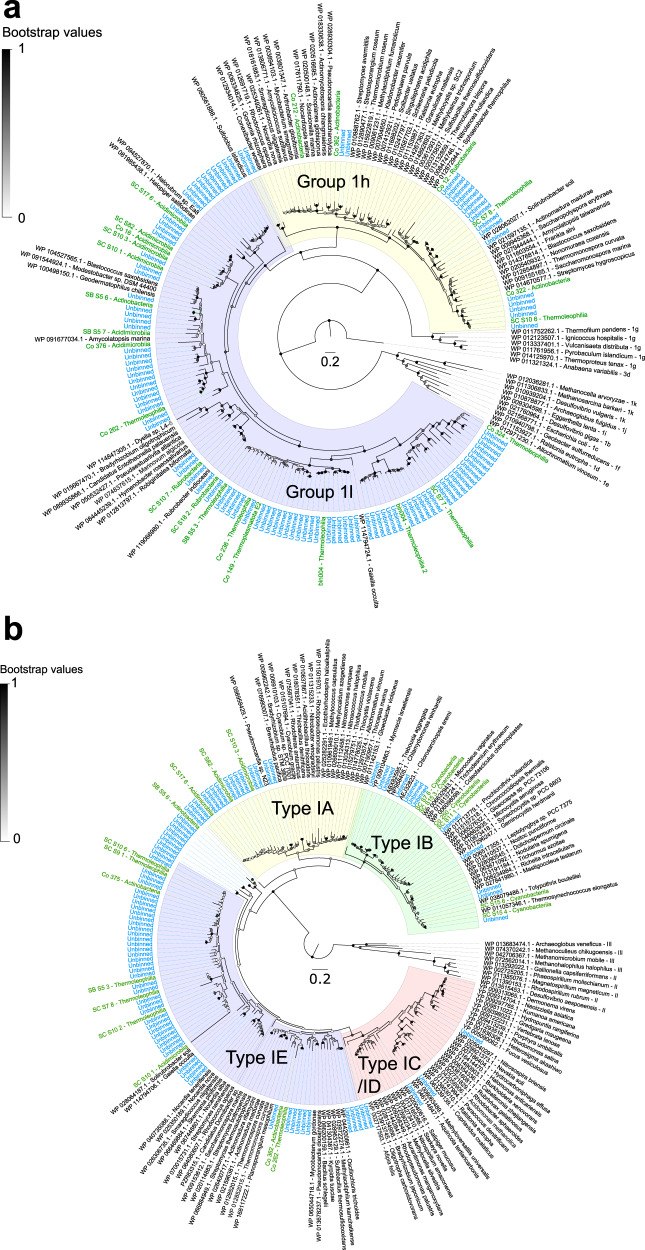
Fig. 3. Maximum likelihood radial phylogenetic trees showing sequence diversity and taxonomic distribution of enzymes responsible for H2 oxidation and carbon fixation.
a Phylogenetic tree of [NiFe]-hydrogenase large subunit amino acid sequences, with a focus on the group 1h (HhyL) and 1l (HylL) high-affinity uptake hydrogenases to which most binned and unbinned sequences affiliated with. b Phylogenetic tree of RuBisCO large subunit amino acid sequences (RbcL), with a focus on the type IA (Acidimicrobiia-affiliated), type IB (Cyanobacteria-affiliated), and type IE (Actinobacteria- and Thermoleophilia-affiliated) enzymes that most binned and unbinned sequences grouped with. Trees show hits to genome bins (red) and unbinned contigs (blue) relative to reference amino acid sequences (grey) (color figure online).