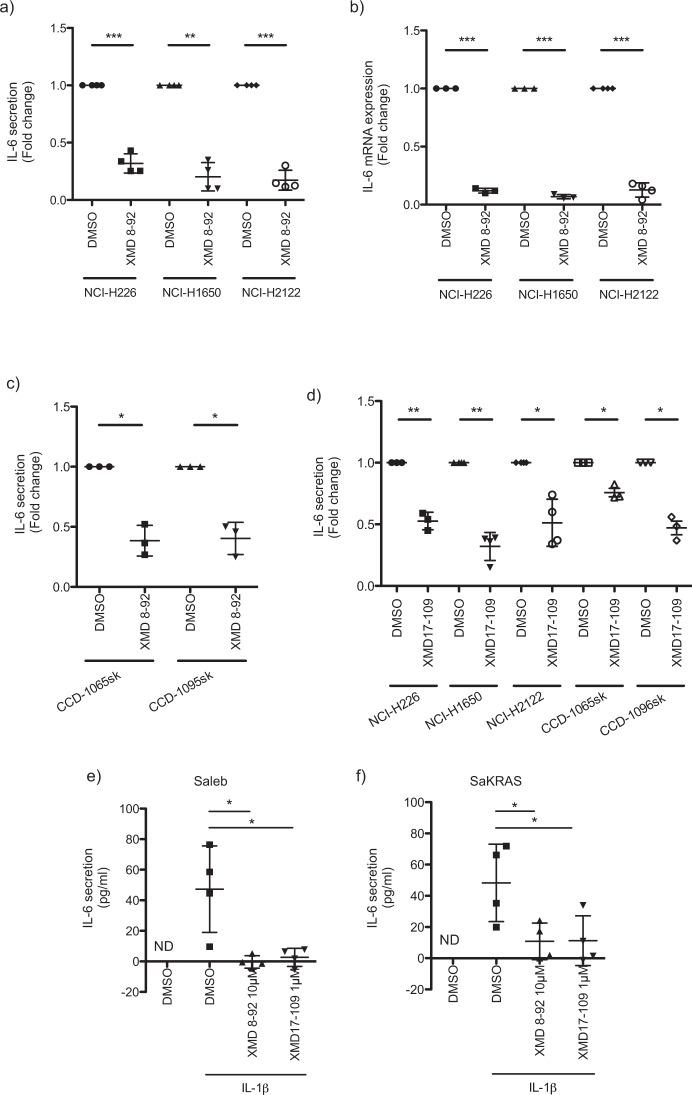
Fig. 5. ERK5 regulates IL-6 secretion from various cancer cell lines.
a The cancer cell lines NCI-H226 and NCI-H1650 were treated for 4 h and NCI-H2122 for 2 h with DMSO or XMD 8-92 (10 µM). After changing the medium to fresh inhibitor-containing medium, supernatant of NCI-H226 and NCI-H1650 was harvested after 4 h, and in the case of NCI-H2122 after 5 h of incubation. IL-6 secretion was studied by ELISA (mean fold change ± SD; n = 4) and b, IL-6 mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR (mean fold change ± SD; NCI-H226/NCI-H1650: n = 3; NCI-H2122: n = 4). c Same as in (a), but with CCD-1065sk and CCD-1095sk fibroblasts (mean fold change ± SD; n = 3). d NCI-H226, NCI-H1650, CCD-1065sk, and CCD-1095sk fibroblasts were pre-treated with XMD 17-109 (NCI-H226, CCD-1065sk, and CCD-1095sk fibroblasts: 10 µM; NCI-H1650, NCI-H2122: 5 µM) for 4 h and NCI-H2122 for 2 h. After changing the medium to fresh inhibitor-containing medium, supernatant of NCI-H226, NCI-H1650, CCD-1065sk, and CCD-1095sk fibroblasts were harvested after 4 h, and in the case of NCI-H2122 after 5 h of incubation. IL-6 secretion was determined by ELISA (mean fold change ± SD; NCI-H226, CCD-1065sk and CCD-1095sk fibroblasts: n = 3; NCI-H1650, NCI-H2122: n = 4). e Saleb, and f, SaKRAS cells were pre-treated with DMSO, XMD 8-92 (10 µM) or XMD17-109 (1 µM) in presence or absence of IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 1 h. The medium was replaced, and treatment was continued for 5 h. The supernatant was collected, and IL-6 secretion was determined by ELISA (mean ± SD; n = 4).