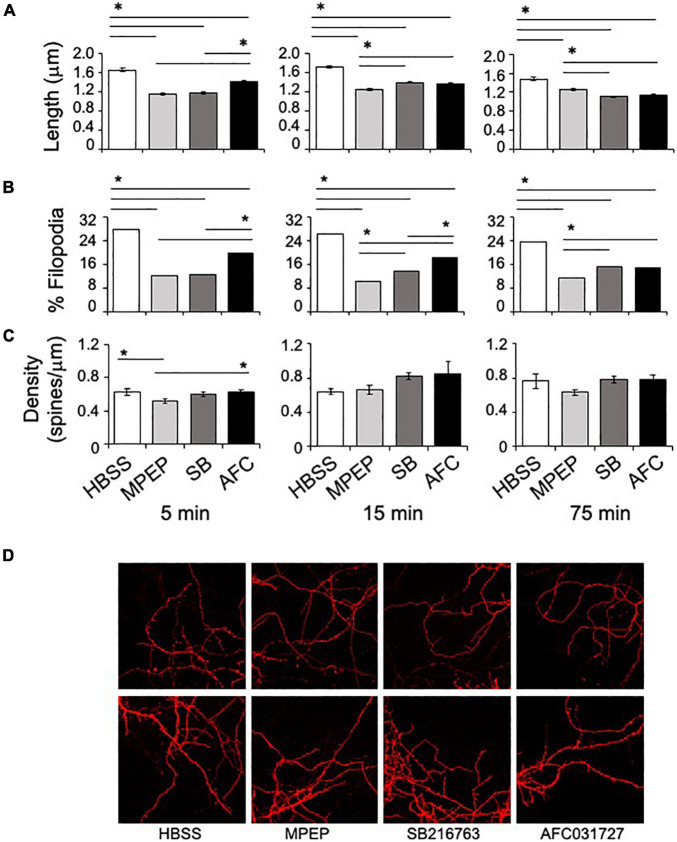
FIGURE 4.
GSK3 inhibitors rescue dendritic spine morphology phenotypes in Fmr1KO mice. (A) Primary cultured Fmr1KO neurons were treated with 25 μM MPEP versus 25 μM SB216763 and 250 nM AFC03127 for 5, 15, or 75 min, stained with DiI and images acquired with an 100x objective. The lengths of dendritic protrusions were quantitated with ImageJ software and plotted against compound treatment. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA [5 min (p < 0.0001, F = 101.8, and dF = 3); 15 min (p < 0.0001, F = 67.61, and dF = 3); and 75 min (p < 0.0001, F = 69.17, and dF = 3)]. Error bars represent SEM. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences by post hoc Tukey tests (p < 0.001). (B) The percentage of filopodia was plotted against compound treatment. Filopodia were defined as protrusions with a width-to-length ratio less than or equal to 0.5. Statistical significance was determined by Chi square analyses (4 × 2 tables) [5 min (p < 0.00001, Chi statistic = 191); 15 min (p < 0.00001, Chi statistic = 165); and 75 min (p < 0.00001, Chi statistic = 101)]. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences by Chi square analyses (2 × 2 tables; p < 0.003). (C) Spine density (# of spines per length of spine) was plotted as a function of compound treatment. Multiple areas of multiple cells were assessed for each treatment. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA [5 min (p = 0.018, F = 3.38, and dF = 3); 15 min (p = 0.14, F = 1.85, and dF = 3); and 75 min (p = 0.18, F = 1.63, and dF = 3)]. Error bars represent SEM. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences by post hoc Tukey tests (p < 0.05). (D) Representative images from 5 min time point at 100x are shown.