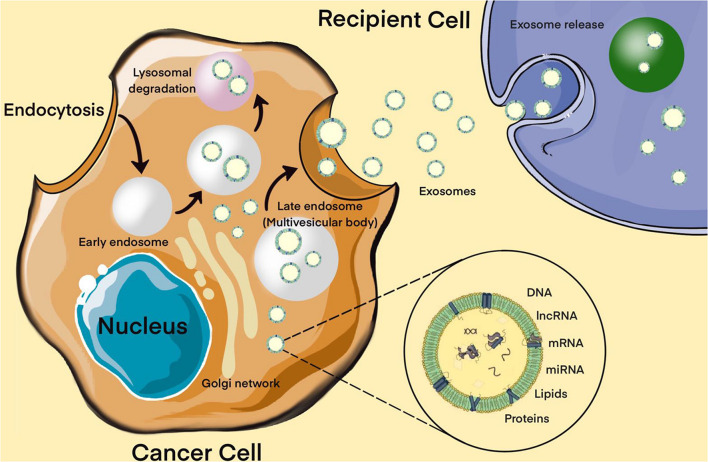
FIGURE 4.
Biogenesis of exosomes. The exosome membrane is formed as a result of the invagination of the early endosome into the membrane. Proteins, lipids, RNA, DNA enter the exosome from the cell cytoplasm. The fate of an endosome depends on the marking of its membrane with certain lipids: if it is labeled with lysobisphosphatidic acid, then its contents will be destroyed, and if ceramides, it will be pushed out of the cell. These processes are controlled by the GTPases of the Rab (G-protein) family, whose various members perform different functions: Rab5 directs the formation of the endosome, Rab7 organizes the degradation of the contents of the multivesicular body (late endosome) in the lysosome, and Rab11, Rab27, and Rab35 are necessary for the secretion of exosomes into the extracellular space. It has been shown that exosomes contain about 4,000 different proteins, more than 1,500 different miRNAs and mRNAs, as well as DNA. Bottom right – enlarged “generalized” exosome.