Figure 2.
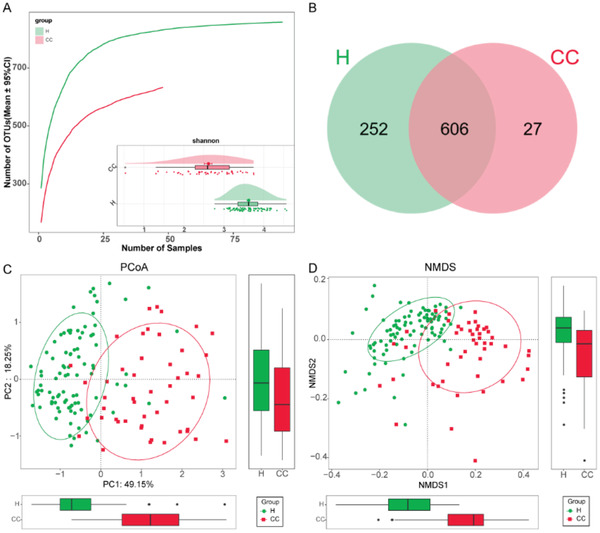
Oropharyngeal microbial diversity of confirmed cases and healthy controls in the discovery cohort. A) Rarefaction analysis showed as the number of samples raised, the number of OTUs approached saturation in CCs (n = 48) and Hs (n = 94). The number of OTUs in CCs was reduced versus Hs. As evaluated by the Shannon index, oropharyngeal microbial diversity was remarkedly reduced in CCs versus Hs (p < 0.001). B) A Venn diagram displaying the overlaps between groups showed that 606 of 885 OTUs were shared in CC and H groups, while 27 of 885 OTUs were unique to the CC group. The PCoA C) and NMDS D) based on OTU distribution showed the oropharyngeal taxonomic composition was conspicuously different between the two groups. COVID‐19, coronavirus disease 2019; Hs, healthy controls; CCs, confirmed cases; OTUs, operational taxonomy units; PCoA, principal coordinate analysis; NMDS, nonmetric multidimensional scaling; centerline, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; error bars, 95% CI.
