Figure 2.
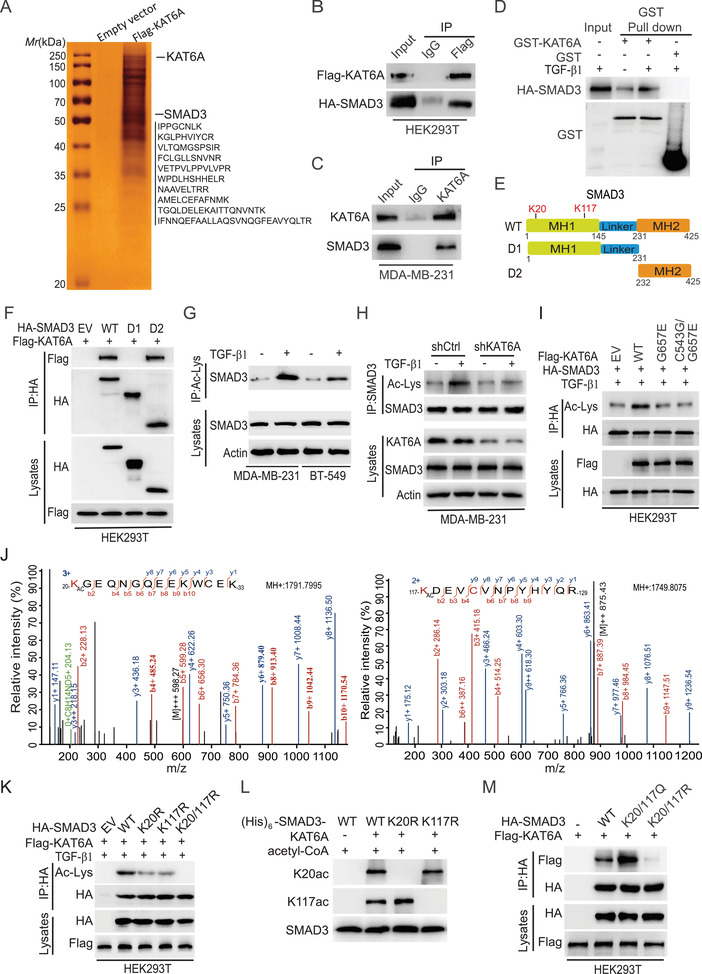
KAT6A acetylates SMAD3 at K20 and K117. A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) and mass spectrometry (MS) analyses of KAT6A‐associated proteins in MDA‐MB‐231 cells. B) Co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) of exogenous KAT6A with SMAD3 in HEK293T cells. C) Co‐IP of endogenous KAT6A with SMAD3 in MDA‐MB‐231 cells. D) In vitro GST pull‐down analysis. Purified GST‐KAT6A or GST proteins were incubated with cell extracts from MDA‐MB‐231 cells stimulated with or without TGF‐β1 (5 ng mL−1, 2 h). E) Schematics of SMAD3 wild type (WT), D1 (MH1 and Linker domain) mutant, and D2 (MH2 domain) mutant. F) IP and WB of KAT6A interaction with SMAD3 WT or mutants. EV, an empty vector control. G) IP and WB for analyzing the acetylated SMAD3 in MDA‐MB‐231 and BT‐549 cells treated with or without TGF‐β1 (5 ng mL−1, 2 h). A pan acetylation antibody (9441S, CST) was used. H) KAT6A knockdown (KD) decreases the acetylation (Ac‐Lys) of SMAD3 in MDA‐MB‐231 cells. I) Effect of acetyltransferase activity‐deficient mutants G657E and C543G/G657E of KAT6A on SMAD3 acetylation. J) MS analysis of acetylation sites of SMAD3 by KAT6A. In vitro acetylated SMAD3 by KAT6A as in panel (D) was purified and then subjected to MS analysis. K) Effect of K20R, K117R, or K20/117R mutation of SMAD3 on KAT6A‐mediated SMAD3 acetylation. L) In vitro KAT analysis using recombinant active KAT6A and (His)6‐SMAD3 WT, K20R, or K117R mutant protein. Acetylation of K20 or K117 was determined by using anti‐K20ac or anti‐K117ac antibodies, respectively. M) IP and WB of KAT6A association with WT SMAD3, the acetylation‐mimetic K20/117Q, or acetylation‐deficient K20/117R mutant. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.
