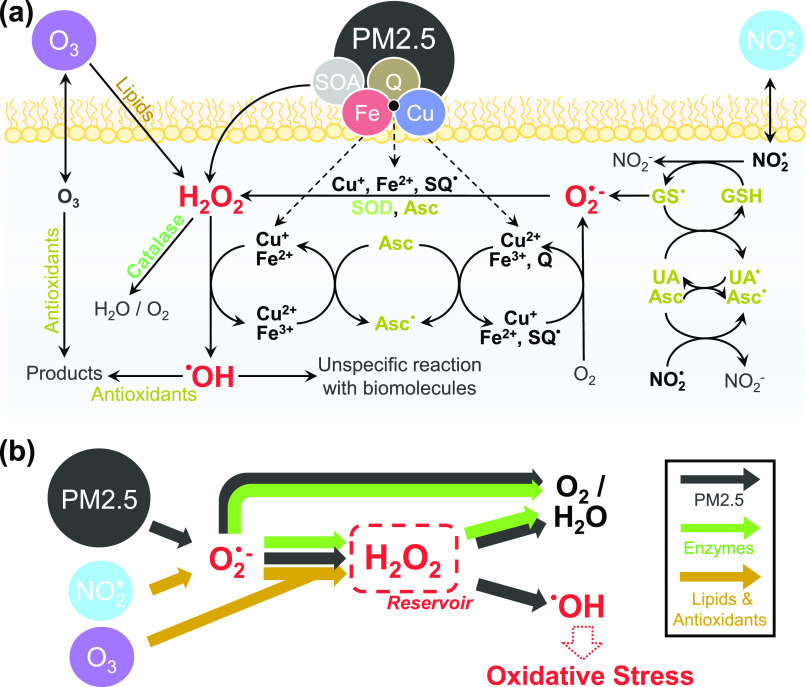
Figure 5.
(a) Production, interconversion, and scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by air pollutants and endogenous molecules in the epithelial lining fluid (ELF). Organic and inorganic constituents of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) can produce, convert, and scavenge ROS. Enzymes (catalase; superoxide dismutase, SOD) intercept ROS through the disproportionation of O2– and the decomposition of H2O2 (green). Antioxidants (ascorbate; glutathione, GSH; uric acid, UA; α-tocopherol, α-Toc) intercept OH, O2–, and H2O2, but the reaction of antioxidants and surfactant lipids with NO2 and O3 can also produce ROS (yellow). Note that PM2.5 constituents are able to convert the relatively stable reservoir species H2O2 into the highly reactive OH radical, which may cause oxidative stress (distress) and physiological damage.30,79 (b) Schematic summary of the main reaction pathways.