Figure 1.
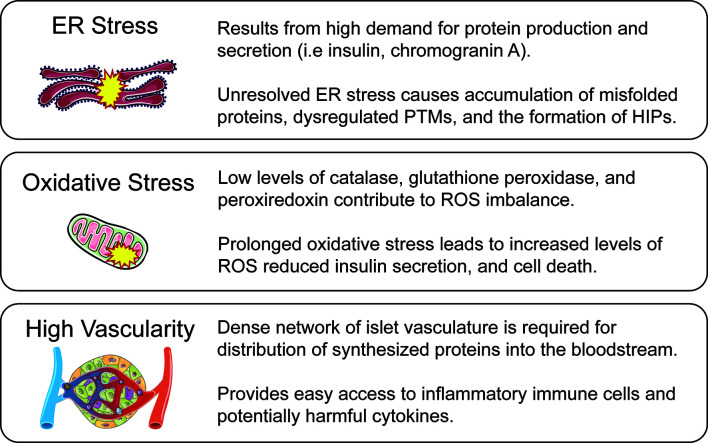
Beta-cell vulnerabilities. While autoimmunity is a major driver of T1D pathogenesis, innate features of beta-cell biology make it a complicit partner in disease progression. These beta-cell characteristics are a result of normal beta-cell function while also active contributors to disease amplification. ER stress is caused by the high protein production and secretory demand of the beta-cell, but in excess leads to misfolded protein response and the generation of HIPs through PTMs. Oxidative stress is caused by an imbalance between the generation of ROS and their detoxification by antioxidants. The reduced antioxidant capabilities of the beta-cell can lead to impaired function and cell death. A densely vascularized environment is required for secretion of insulin and other peptides directly into the bloodstream, but creates a direct dialogue between the beta-cell and potentially harmful immune cells and inflammatory cytokines which may further lead the cell toward stress and apoptosis.