Figure 6. Biomechanical function of aortas of MFS mice systemically treated with BT173.
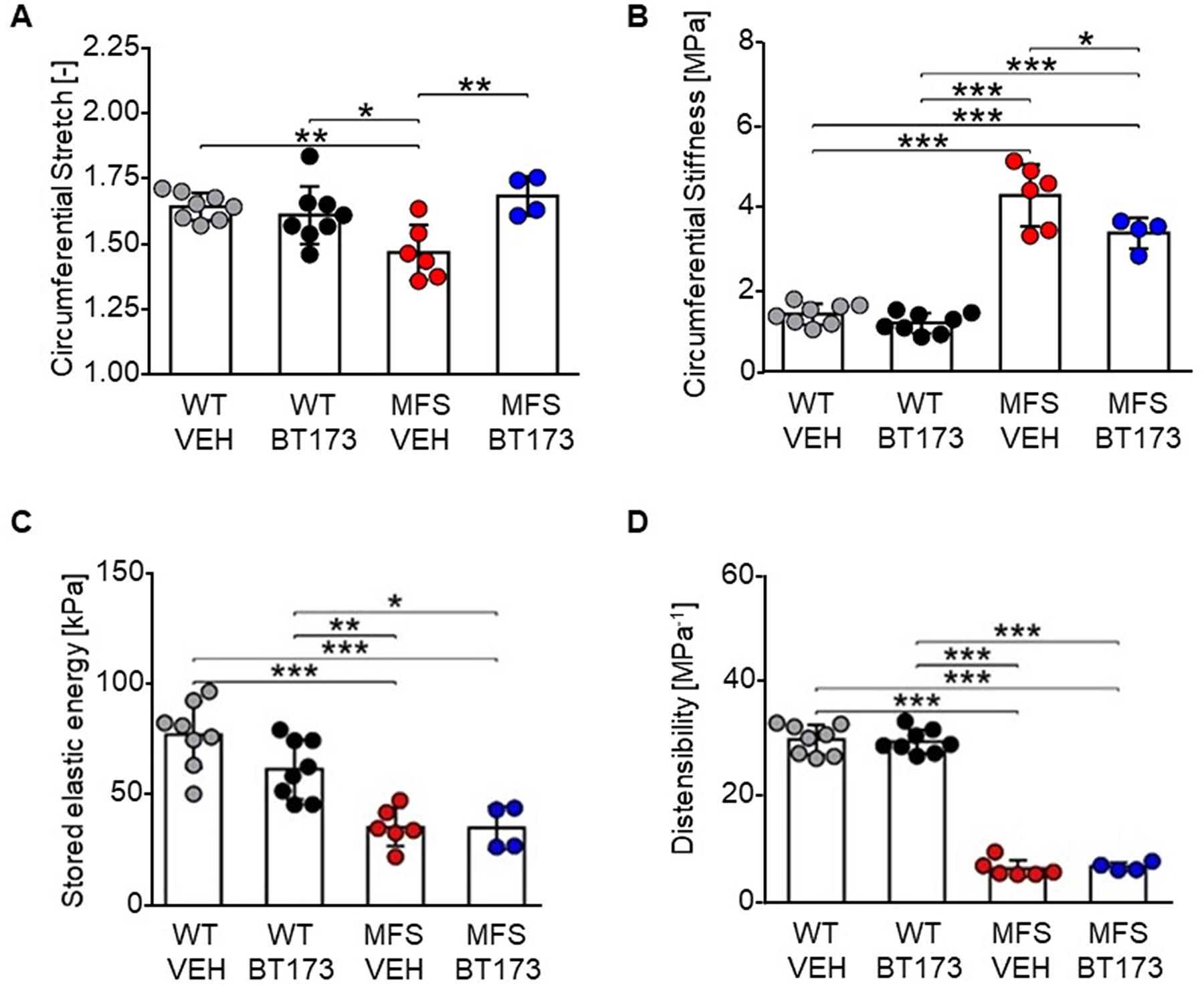
Results of ex vivo biaxial mechanical testing. Dots represent individual animals; bars represent mean ± SD. Treatment increased circumferential stretch (A) and decreased circumferential material stiffness (B) in MFS. Elastic energy storage capacity (C) and distensibility (D) were not affected by BT173 treatment. All metrics (n= 4–8) were evaluated at the individual in vivo values of the axial stretch. Metrics in panels A–C were calculated at the group-specific systolic pressure; distensibility (D) was calculated as(Ds − Dd)/(Dd × (Ps − Pd)), with P and D indicating pressure and inner diameter, and subscripts s and d systolic and diastolic, respectively. Additional biomechanical data are included in Supplemental Table VII. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post-hoc tests were employed to determine statistically significant differences (p≤0.05), which are indicated by asterisks (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001).
