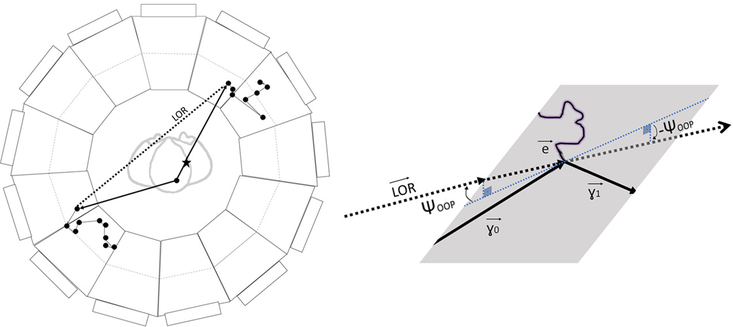
Figure 4:
The LOR in the case of in-patient gamma-ray scattering. The positron annihilation point is marked by a star. The true gamma trajectories are represented by solid lines, and the reconstructed LOR connecting the two measured gamma interaction points by a dashed line. The scattered gamma (lower left-hand quadrant) will have a decreased energy and a longer flight path (larger TOF). The inset shows that a gamma-ray scattering in the patient produces a non-zero component of the LOR out of the plane defined in the detector module by the scattered electron and gamma, i.e. . Alternatively, the out-of-plane angle (OOP) is not zero. In addition, the polarizations of the gammas are correlated through their initial state entanglement.