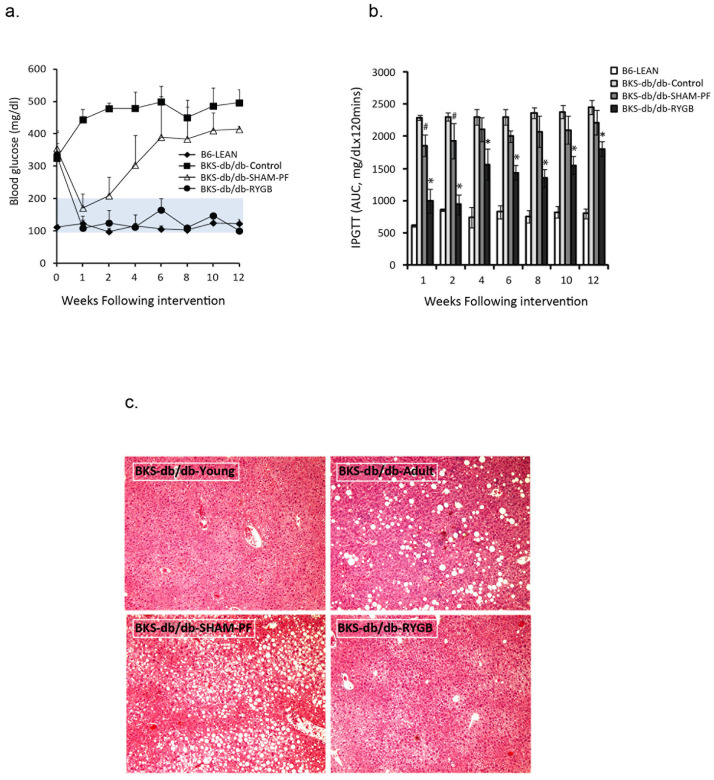
Fig 2. RYGB maintains normoglycemia and improves glucose tolerance and liver steatosis when performed in young prediabetic BKS-db/db mice (6 weeks of age).
a. Blood glucose levels. B6-LEAN, Chow-fed WT C57BL/6 (n = 5); BKS-db/db-Control, untreated BKS-db/db mice (n = 5); BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF, BKS-db/db mice with sham surgery and pair-feeding (n = 6), and BKS-db/db-RYGB, BKS-db/db mice with RYGB (n = 8). Mice at 6 weeks of age was defined as 0 week. The shaded area represents a normal range of lean mouse blood glucose levels. BKS-db/db-RYGB vs. BKS-db/db-Control p < 0.001 from the 1st week to 12 weeks post-surgery. BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF vs. BKS-db/db-Control, p < 0.01 at the first two weeks (p < 0.05), p > 0.05 from 4 to 10 weeks and p < 0.05 at 12 weeks post-surgery. b. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests (IPGTT). B6-LEAN, C57BL/6 mice (n = 5); BKS-db/db-Control, untreated BKS-db/db mice (n = 5); BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF (n = 5), and BKS-db/db-RYGB (n = 7) mice. *: BKS-db/db-RYGB vs. BKS-db/db-Control and BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF, p < 0.001 and #: BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF vs. BKS-db/db-Control, p < 0.05. c. Liver H&E stanning (x 100). BKS-db/db-Young, young prediabetic BKS-db/db (6 weeks of age); BKS-db/db-Adult, adult diabetic BKS-db/db (12 weeks of age); BKS-db/db-SHAM-PF (12 weeks post-surgery) and BKS-db/db-RYGB (12 weeks post-surgery). The figures represent one of three pathological examinations in each group).