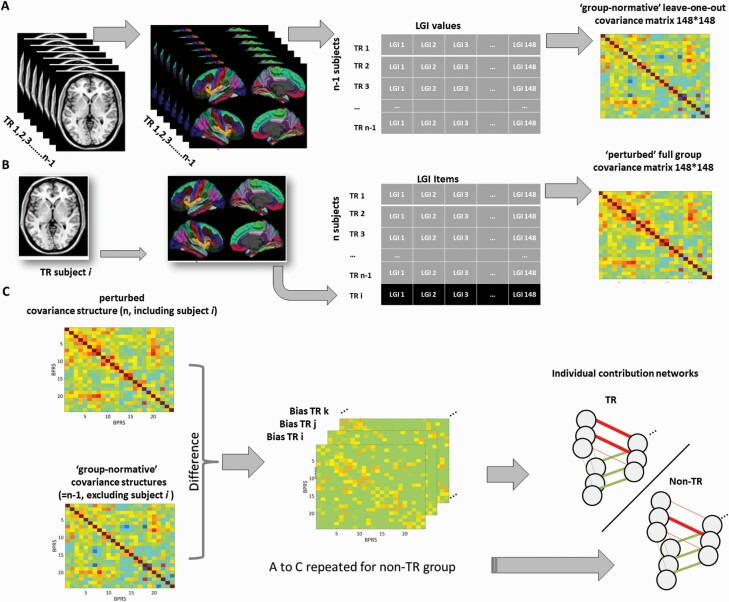
Fig. 1.
Depicts 3 steps (referred to as A, B, and C) followed to construct an individual-specific LGI network in the present study. (A) For a single group of (N-1) subjects (treatment resistance [TR] or non-TR), a specific group-based network is constructed by the correlations between LGI values based on regional LGI measures from 148 parcellations in this group, with the exclusion of a single subject i. This group network (based on N-1 matrix) has the “normative” covariance structure of that group’s gyrification pattern. (B) A new subject i belonging to that patient group is added to the group, and the perturbed network with this additional individual is constructed in the same way as the (N-1) matrix. The difference between the (N) and the (N-1) network is due to the individual i (or j or k…). (C) An individual contribution-based network is constructed using the difference of the corresponding edge between the (N) and (N-1) matrix. For illustrative purposes, only one group (TR) and only 3 nodes are shown. LGI-based networks in this study were made of 148 nodes, each node representing a single region of the parcellation scheme.