Figure 1:
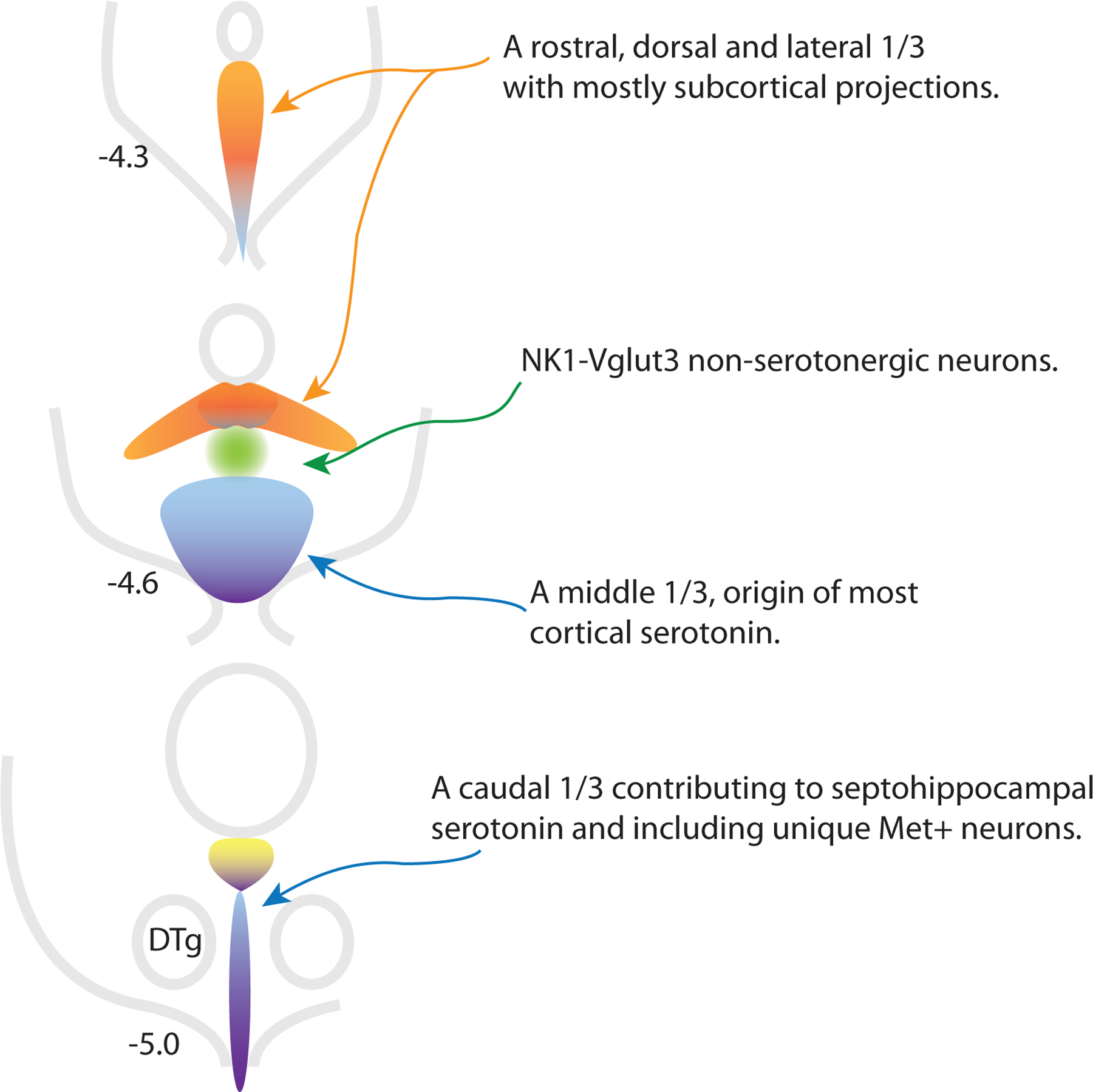
Schematic representation of different zones of the dorsal raphe nucleus from rostral (top) to caudal with distance from Bregma noted. New data link the lateral wings of the DR with neurons in rostral and dorsal locations in the nucleus, these areas may be more heavily populated by less Vglut3 and transitional neurons (groups 2–6, orange). NK1-Vglut3 neurons (group 13, green) have Pet1 lineage but express low levels of genes associated with serotonergic neurotransmission, but would not be identified as serotonergic by other criteria. These neurons may help coordinate ascending serotonin function with dopaminergic activity. The largest cluster of serotonin neurons likes in the middle-ventral part of the nucleus and is the major source of cortical serotonin (blue, more Vglut3 neurons including groups 9–11). The caudal third of the DR (purple, probably more heavily groups 7, 8, and 14) resembles the MR in connectivity, although Met+ neurons at the base of the aqueduct have many unique characteristics (yellow, group 12). Dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden (DTg).
