FIGURE 1.
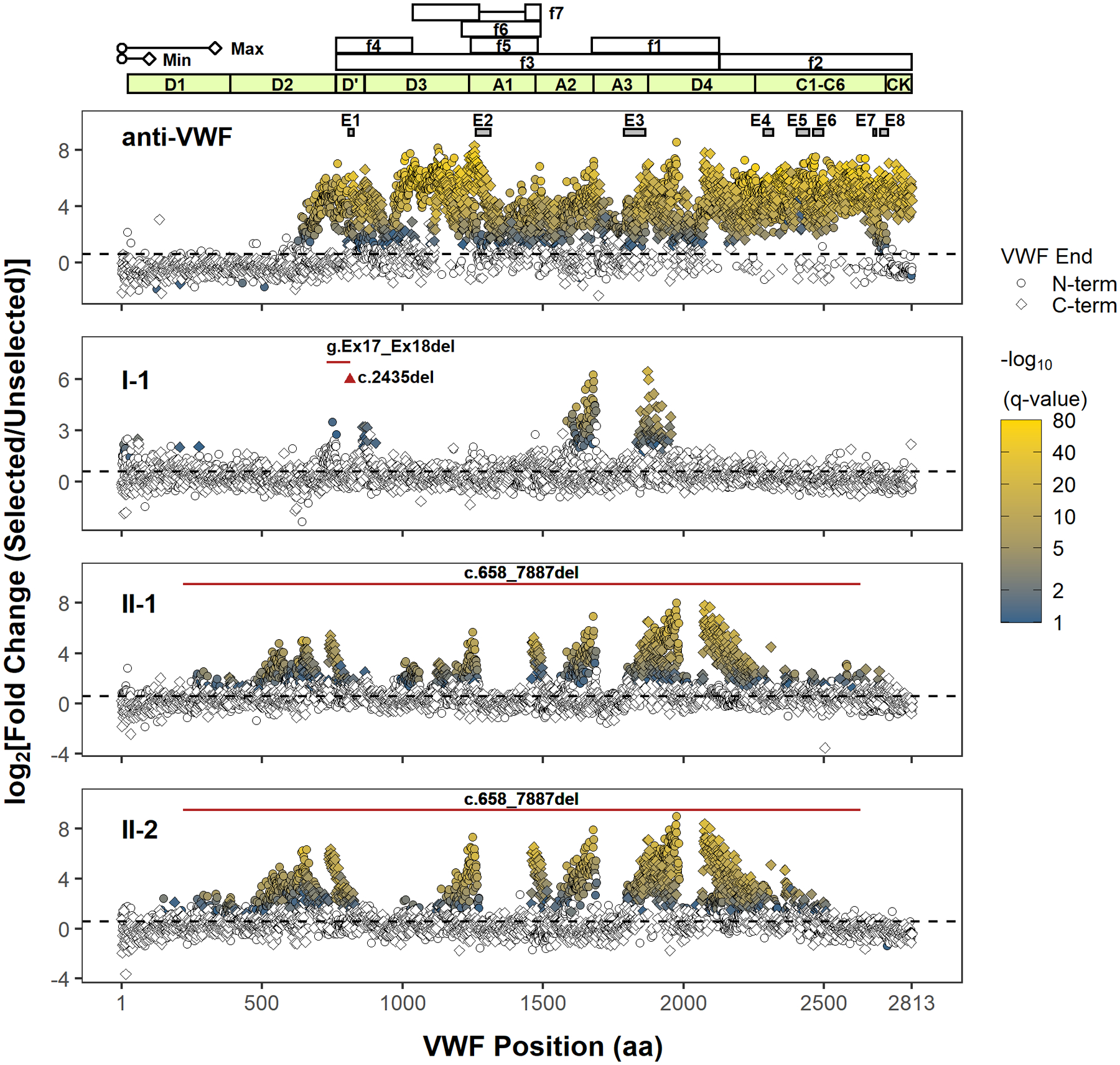
Next-generation DNA sequencing analysis of phage display identifies immunoreactive regions in VWF. Only the position of the first (N-terminal) or last (C-terminal) residue within the identified VWF fragment is shown. The approximate minimal (min, ~100 amino acids) and maximal (max, ~333 amino acids) lengths of phage displayed VWF peptides (depiction scaled according to the x-axis) are determined from the size range of VWF cDNA fragments subcloned into the phagemid. However, the phase of N- and C-termini of individual VWF fragments (i.e., which N-terminus is paired with which C-terminus) cannot be determined because of the fragmentation of PCR amplicons of phage DNA for NGS, limiting the delineation of unique epitopes. The coordinates of proteolytic VWF fragments, f1–f7, used to epitope map anti-VWF alloantibodies in prior reports are shown (f1: G1674-E2128; f2: E2129-K2813; f3: S764-E2128; f4: S764-R1035; f5: L1243-G1481; f6: V1212-K1491; f7: K1036-R1274, A1437-K1491).10–13 The VWF domain boundaries are annotated in light green. The black dashed line denotes a fold change of 1.5. Terminal residues of phage displayed VWF fragments are marked (VWF end) according to their location and enrichment. Only VWF fragment termini with a significant fold change (FDR adjusted p value < .1) are indicated in shading from blue to yellow, which scales with the significance of fold change (−log10(q value)). A polyclonal anti-VWF antibody (anti-VWF) recognizes fragments spanning the mature VWF sequence. Epitopes E1–E8 were previously identified by conventional phage display for the same antibody, and their coordinates are shown as gray boxes.16 The regions for E1–E8 are magnified in Figure S4. VWF inhibitors from type 3 VWD patients (I-1, II-1, and II-2) bind distinct regions in VWF. The location of the patients’ genetic deletion(s) is marked according to the corresponding VWF codon (red triangle for point deletion or red solid line for contiguous deletion). Note that the clustering of significantly enriched termini supports localization of a series of reactive VWF fragments whose internal sequences are graphically depicted as gaps between the clusters (e.g., the immunoreactive region in A3 for I-1 is bounded by clusters of significantly enriched N- and C-terminal residues on the left and right, respectively). Abbreviations: FDR, false discovery rate; NGS, next-generation sequencing; VWD, von Willebrand disease; VWF, von Willebrand factor
