Figure 1.
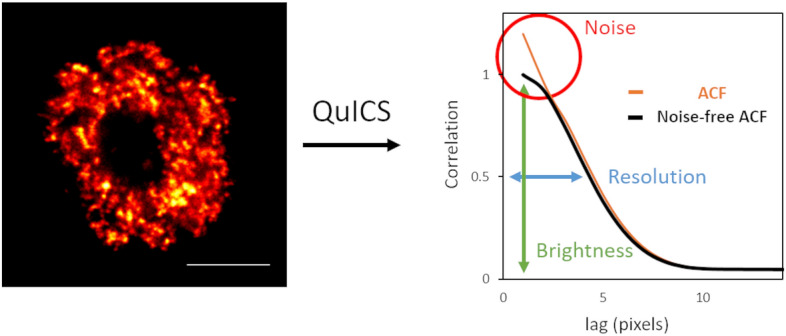
Autocorrelation function (ACF) as a source of information about image quality. (left) Representative image of U937-PR9 cell upon staining of DNA replication foci through incorporation of EdU labeled with Alexa azide 488 (Click reaction). Scale bar represents 3 µm. (right) Schematic representation of the application of the QuICS algorithm to an image of a nuclear process (DNA replication sites). The algorithm calculates a radial autocorrelation function (ACF, orange line) and performs a Gaussian fit of the estimated noise-free ACF (black line). The three parameters that are extracted are: the Resolution (in blue), calculated from the width of the noise-free ACF, the Brightness (in green), calculated from the amplitude of the noise-free ACF, and the Noise (in red), calculated from the difference in amplitude between the ACF and the noise-free ACF.
