Figure 10.
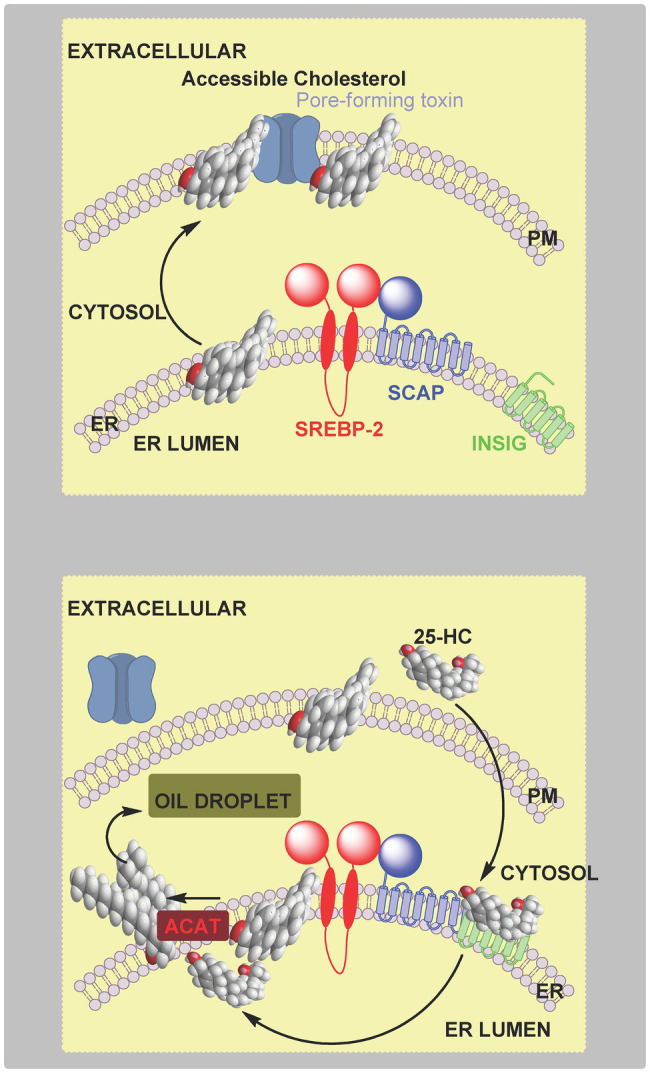
Cartoon representation of the protection by 25-HC of macrophages and neutrophiles against pore-forming toxins. Upper panel, pore-forming toxin binds to accessible cholesterol in the plasma membrane, oligomerises and create a pore, ultimately leading to cell death. Lower panel, 25-HC generated by macrophages in response to infection rapidly crosses the cell membrane, and (i) inhibits SREBP-2 processing leading to reduced cholesterol synthesis and (ii) activates ACAT/SOAT and cholesterol esterification, in combination leading to a reduction in plasma membrane accessible cholesterol. The consequence is reduced binding of pore-forming toxins to the plasma membrane and protection of the cell. 25-HC can also activate LXR to enhance cholesterol export and can encourage the ubiquitination and degradation of HMG-CoA reductase to repress cholesterol synthesis (not shown).
