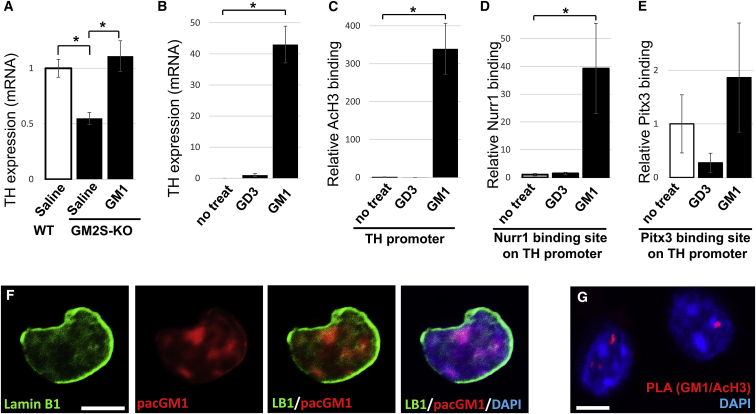
Figure 6.
Ectopic GM1 induces epigenetic activation of the TH gene via recruitment of dopaminergic transcription factor Nurr1
(A) Reduced TH expression in substantia nigra of GM2S-KO mouse (8 months old), and intranasal GM1 administration (5 mg/kg/day for 28 days) restored TH levels. (B–E) Neuro 2a cells were cultured in the presence of gangliosides (5 μM of GM1 or GD3) for 24 h. (B) mRNA analysis for TH expression. Enrichment of epigenetic markers and recruitment of transcription factors in the TH gene promoter were analyzed by ChIP assays with anti-AcH3 (C), anti-Nurr1 (D), or anti-Pitx3 (E), followed by qPCR analyses. (F) Photoactivatable and clickable GM1 (pacGM1) was tagged with TAMRA (carboxytetramethylrhodamine) on isolated nuclei on Neuro 2a cells. pacGM1 technique is able to prove that exogenous GM1 (red) can be delivered inside the nucleus. (G) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) using anti-GM1 (mouse antibody, MINUS) and acetylated histone H3 anti (rabbit antibody, PLUS) in isolated nuclei from adult mouse brain. Values were normalized to control levels and are means ± SE (n = 3-6 independent experiments/group; two-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison test). ∗p < 0.05. Scale bars, 5 μm.