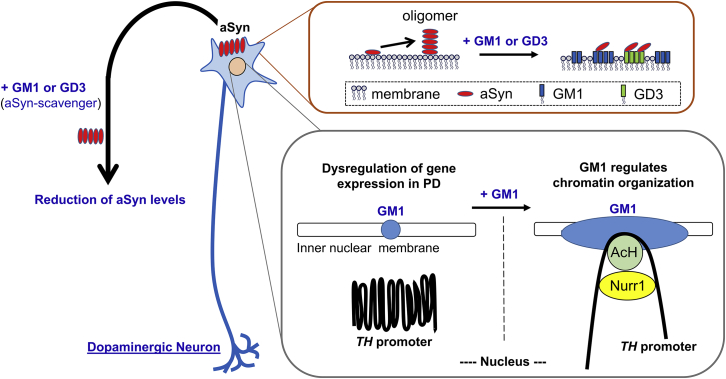
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of intranasal ganglioside therapy
Gangliosides prevent aSyn accumulation, and a supportive ganglioside composition will reduce aSyn neurotoxicity. GM1 strongly inhibits, and GD3 partially inhibits, aSyn accumulation. GM1 facilitates binding of acetylated histones (AcHs) and Nurr1 transcription factor on the TH promoter to increase TH expression via opening chromatin. The nuclear GM1-lipid domains may serve as a docking site at the nuclear periphery for specific active chromatins for dopaminergic neurons and for maintaining neuronal functions. Thus, ganglioside therapy is a two-pronged approach that effectively treats PD by decreasing cytotoxic aSyn and sustaining the function of dopaminergic neurons.