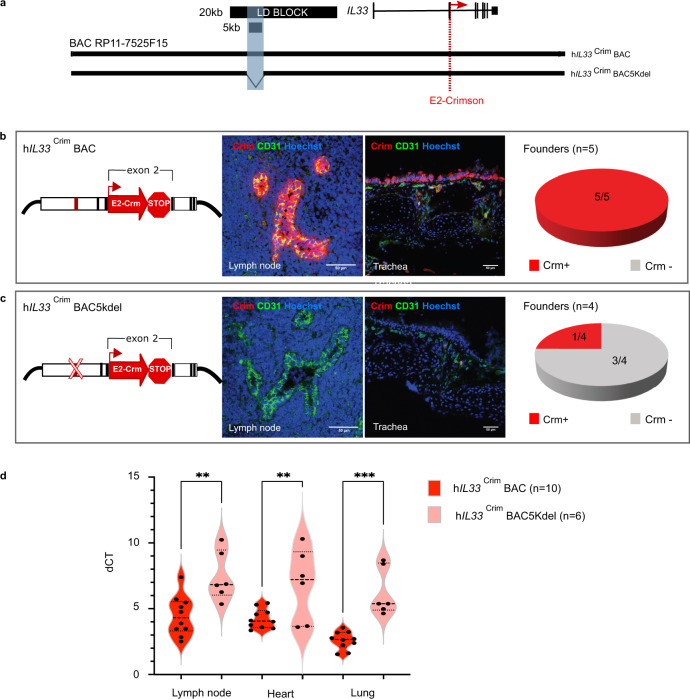
Fig. 2. The IL33-containing BAC in transgenic mice encodes human-specific regulatory patterns and demonstrates the importance of the 5 kb noncoding segment for proper IL33 expression.
a Schematic of human BAC clone RP11-725F15 (166 kb) spanning the entire coding region of IL33 and its upstream region including the 20 kb asthma-associated interval and the 5 kb region of interest shaded in blue (black bars). To produce a human IL33 reporter strain, a cassette containing E2-Crimson with a stop sequence was inserted into exon 2, in frame with the IL33 translational start site (red dotted line). Transgenic mice were generated with either the full BAC (hIL33CrimBAC) or a BAC containing a deletion of the 5 kb interval within the LD block (hIL33Crim BAC5kdel). b, c Immunofluorescence staining of mouse peripheral lymph node sections (left panels) and trachea tissue sections (right panels) of E2-Crimson in hIL33Crim BAC mice (b) or hIL33Crim BAC5kdel (c). Representative founder BAC transgenic lines are shown. Sections were stained with anti-E2-Crimson (red) and the mouse endothelial cell marker CD31 (green). Hoechst 33342 staining for nuclei is in blue. Pie charts show the distribution of Crimson expression (Crm) in each “humanized” BAC mouse line. d qPCR analysis of E2-Crimson mRNA obtained from lymph node, heart, and lung from both BAC strains is shown. Violin plot shows average dCT values (Crimson/Ppia) obtained from animals containing either the full BAC or the 5 kb deletion (n = 10 biologically independent animals for full BAC and n = 6 biologically independent animals for 5 kb deletion). Center line: median; box limits: upper and lower quartiles; whiskers: 1.5 × interquartile range. **p = 0.0017 (lymph node); **p = 0.0066 (heart), ***0.0001; one-way ANOVA with post hoc Sidak multiple comparison test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.