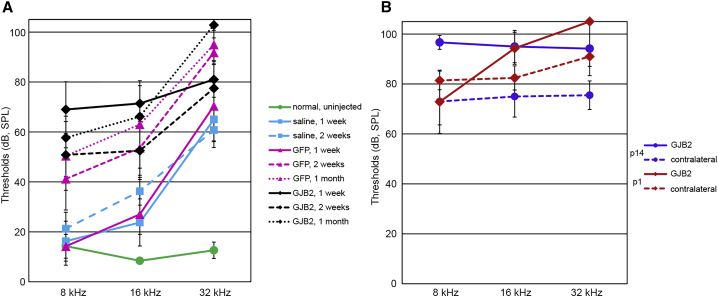
Figure 8.
Anc80-GJB2-FLAG does not improve hearing in iCKO mouse ears.
Thresholds detected by ABR audiometry in three frequencies in control animals (A) and iCKO with tamoxifen given at P1 or P14 (B). The green line in (A) depicts the thresholds for un-injected iCKO mice. All treatments induced significant hearing loss compared with normal ears (A, green line), as demonstrated by saline-treated ears at 1 week (cyan, solid line; Table 2, row 1, p = 0.003). Saline injection elevated thresholds at 16 and 32 kHz, but GFP treatment at 2 weeks or later (pink dashed and dotted lines) and GJB2 treatment at all time points (black lines) had elevated thresholds at all three tested frequencies. Thresholds in GFP-treated ears were not significantly higher than in saline-treated ears at 1 week after injection (Table 2, row 3, p = 0.954) but were significantly higher by 2 weeks after injection (Table 2, row 4, p = 0.038). Hearing loss at 1 week was greater after GJB2 treatment (solid black line) than GFP (solid pink line), which was very significant (Table 2, row 6, p < 0.001). Hearing loss at later time points after GJB2 treatment (dashed and dotted black lines) was not significantly greater (Table 2, rows 7 and 8, p > 0.2). Ears that received GJB2 treatment after loss of connexin 26 was induced at P1 (part B, red) had greater hearing loss after GJB2 treatment (Table 2, row 9, p = 0.047) because of elevated thresholds at 16 and 32 kHz. The effect of GJB2 treatment was not significant in ears with connexin 26 loss induced at P14 (purple lines; Table 2, row 10, p = 0.692), primarily because of marginally greater loss in contralateral ears. Thresholds for GJB2 treated ears (B, solid lines) did not differ as function of the age at which connexin loss was induced (Table 2, row 11, p = 0.175).