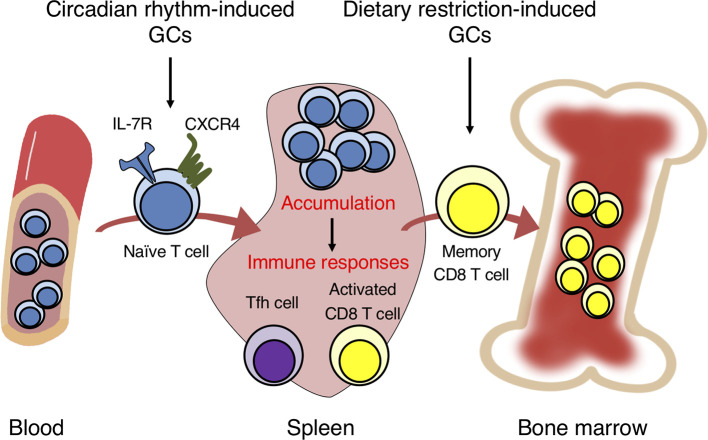
Figure 1.
Glucocorticoids in circadian rhythm and dietary restriction induce the migration of naïve and memory T cells into the spleen and bone marrow. GCs induced by circadian rhythm promote the homing of naïve T cells into secondary lymphoid organs from peripheral blood by inducing the expression of IL-7R and CXCR4. The T cell accumulation induces strong immune responses by activated CD8 T and follicular helper T (Tfh) cells against bacterial infection and soluble antigens. GCs induced by dietary restriction trigger the egress of memory CD8 T cells from secondary lymphoid organs and homing into the bone marrow. The accumulation in the bone marrow enhances the survival and response of memory CD8 T cells.