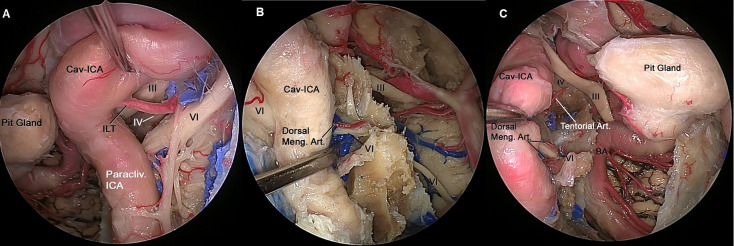
Figure 4.
(A) Endoscopic view of left CS showing the neurovascular relationships in the lateral compartment. The ILT arising from the midportion of the horizontal segment of the intracavernous ICA, and its branches can be identified running from medial to lateral where they distribute along the lateral wall of the CS and supplies to the of CN III, CN IV and distal CN VI. (B) The paraclival ICA is retracted laterally to expose CN VI inside Dorelo’s canal. Dorsal meningeal artery (Dorsal Meng. Art.), a branch from MHT, which is located in the posterior compartment of cavernous sinus and supply proximal segment of CN VI at the level of Dorelo’s canal. (C) Endoscopic view of right CS showing the neurovascular relationships in the superior and posterior compartment of the CS. The Cav-ICA is retracted laterally. The tentorial artery and dorsal meningeal artery can be identified running in the superior and posterior compartment of the CS, respectively. The dorsal meningeal artery supplying proximal segment of CN VI at the level of Dorelo’s canal and the tentorial artery supplying the CN IV are shown. BA, Basilar Artery; Cav, Cavernous; CAV-ICA, Cavernous Internal Carotid Artery; CN, Cranial Nerve; Dorsal Meng. Art, Dorsal Meningeal Artery; ICA, Internal Carotid Artery; ILT, inferolateral trunk.