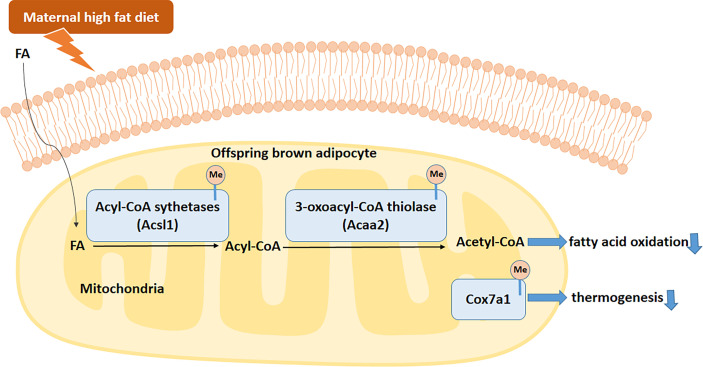
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism by which maternal HFD disrupts brown adipose tissue (BAT) fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and thermogenesis in male offspring. Fatty acids (FAs) enter brown adipocytes and are activated by acyl-CoA sythetases, including Acsl1, to form acyl-CoAs. Then acyl-CoAs were catabolized to acetyl-CoAs by acyl-CoA dehydrogenases, such as Acaa2. Maternal HFD active the methylation of offspring BAT FAO related enzymes, such as Acsl1 and Acaa2. Meanwhile, Cox7a1 gene methylation in offspring BAT was also active by maternal HFD. To sum up, maternal HFD disturbs the BAT FAO and thermogenesis through activated specific gene DNA methylation. FA, fatty acid.