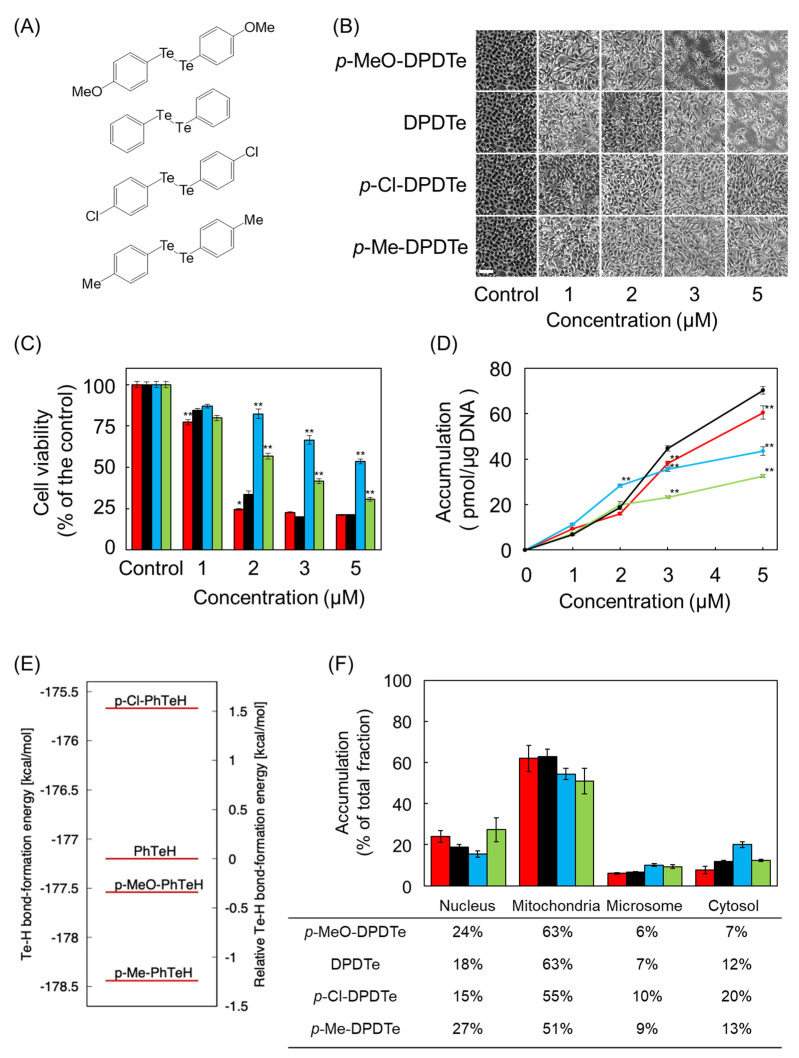
Figure 4.
Effect of substitution on cytotoxicity and intracellular accumulation of DPDTe. (A) Structure of p-MeO-DPDTe, DPDTe, p-Cl-DPDTe, and p-Me-DPDTe. (B) Morphological observation (bar = 50 µm), (C) viability of vascular endothelial cells, and (D) intracellular accumulation of p-MeO-DPDTe, DPDTe, p-Cl-DPDTe, and p-Me-DPDTe. Vascular endothelial cells were treated with p-MeO-DPDTe (red), DPDTe (black), p-Cl-DPDTe (blue), and p-Me-DPDTe (green) (1, 2, 3, or 5 µM) for 24 h. (E) Te–H bond formation energies in p-MeO-PhTeH, PhTeH, p-Cl-PhTeH, and p-Me-PhTeH. (F) Accumulation of p-MeO-DPDTe, DPDTe, p-Cl-DPDTe, and p-Me-DPDTe in cellular fractions. Vascular endothelial cells were treated with 2 µM of p-MeO-DPDTe (red), DPDTe (black), p-Cl-DPDTe (blue), and p-Me-DPDTe (green) for 24 h. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three replicates. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with the corresponding DPDTe treatment.