Figure 9.
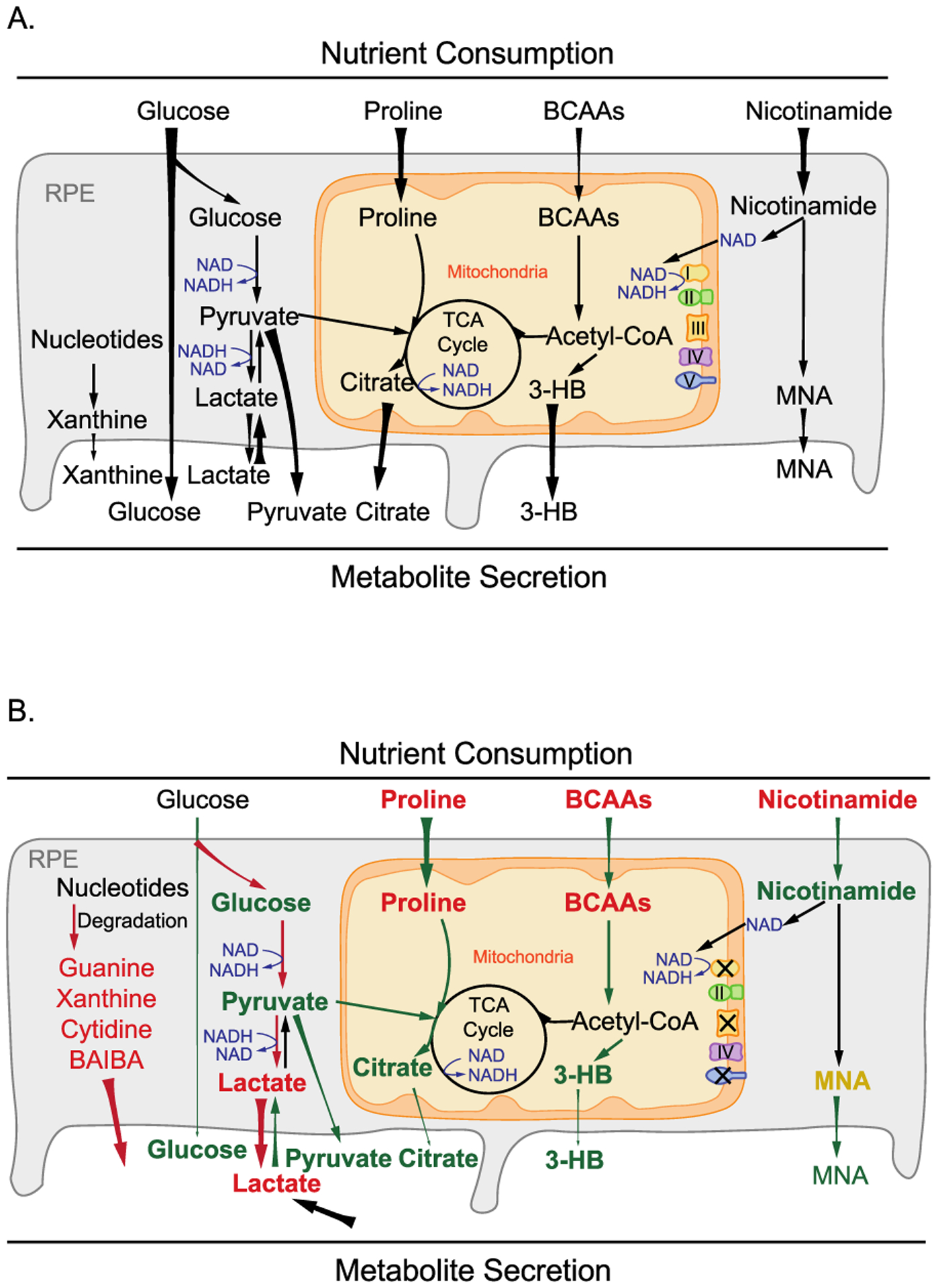
Schematic for the role of mitochondrial metabolism in nutrient consumption and metabolite export. (A) Healthy RPE mitochondria use different nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, lipids, and nicotinamide and export mitochondria-derived metabolites including citrate, isocitrate, and 3-HB to the outer retina. (B) When mitochondrial respiration is inhibited, RPE cells consume more glucose into lactate but use fewer other fuels, leading to a substantial reduction in exporting glucose, citrate, and 3-HB. Moreover, large amounts of lactate and nucleosides such as guanine, guanosine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and BAIBA were exported out of RPE cells.
