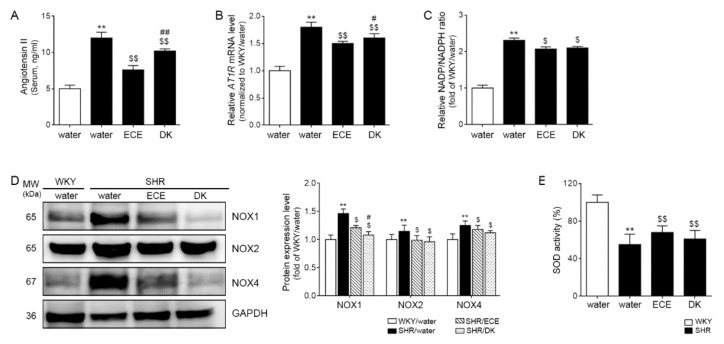
Figure 1.
Regulatory effect of ECE and DK on serum Ang II, AT1R, and ROS production in the muscle of SHRs. (A) The Ang II level in serum increased following SHR/water and decreased following ECE or DK treatment; (B) the expression levels of AT1R mRNA in muscle increased following SHR/water and decreased following ECE or DK treatment. The mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR, normalized versus actb, and expressed relative to the WKY/water group levels. (C) The NADP+/NADPH ratio in muscle was increased following SHR/water and decreased following ECE or DK treatment. (D) The expression levels of protein in ROS production (Nox1, NoxX2, and Nox4) in muscle were increased in SHR/water groups and decreased in ECE- or DK-treated groups via immunoblotting. (E) The SOD activity in the muscle decreased following SHR/water and increased following ECE or DK treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SD. For each of the 4 groups. n = 5. **, p < 0.01, vs. WKY/water; $, p < 0.05 and $$, p < 0.01, vs. SHR/water; #, p < 0.05 and ##, p < 0.01, vs. SHR/ECE (Mann–Whitney U test). AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; DK, dieckol; ECE, Ecklonia cava extract; NADP, nicotinamide-adenin-dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, NADP hydrogen; Nox, NADPH oxidase; SHR, spontaneously hyper-tensive rat; SOD, superoxide dismutase; WKY, Wistar Kyoto rat.