Table 1.
Pharmacological characteristics of HNMT inhibitors.
| Inhibitor | IC50 | Effects on Histamine Brain Levels | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
Metoprine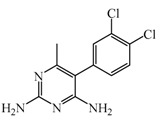
|
100 nM | Metoprine administered at 10 mg/kg (orally) can increase histamine levels, being the highest 5 h after administration and correlates with peak drug levels in the brain. Histamine levels are still elevated more than 2-fold 4 h after administration of the drug. | [144] |
Amodiaquine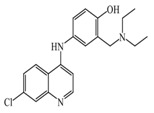
|
400 nM | Antimalarian agent, potent HNMT inhibitor by in vitro studies. However, amodiquine did not change the endogenous histamine level in the rat brain. | [148] |
Quinacrine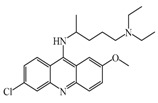
|
160 nM | Quinacrine, a drug that inhibits HNMT in vitro, has little or no effect on the levels in vivo of histamine. | [149] |
Etoprine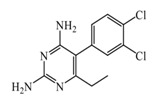
|
760 nM | Etoprine inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Etoprine can cross the BBB; however, its effect on histamine brain level has not been explored. | [150] |
Dimaprit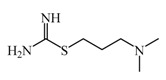
|
8 μM | Dimaprit, an H2R antagonist, is a potent HNMT inhibitor. Dimatiprit increases histamine brain levels after intracerebroventricularly administration in rats. | [151] |
SKF91488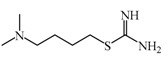
|
1.85 μM | Due to the low permeability of the BBB SKF91488, research for this compound has been limited. | [152] |
