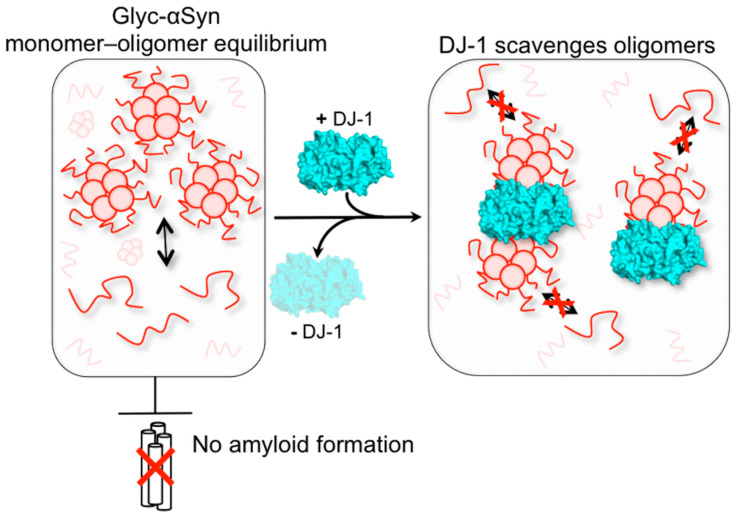
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism for DJ-1’s impact on ac-αSyn glycation. (Left) Glyc-ac-αSyn spontaneously forms oligomers that are in equilibrium with glyc-ac-αSyn monomers. Glyc-ac-αSyn does not form amyloid fibrils, although the oligomers have been shown to be harmful to neurons. (Right) Upon addition of DJ-1, DJ-1 scavenges glyc-ac-αSyn oligomers, preventing their interactions with glyc-ac-αSyn monomers. This allows glyc-ac-αSyn monomers to be free in solution. Removal of DJ-1 from the system restores the glyc-ac-αSyn monomer–oligomer interactions.