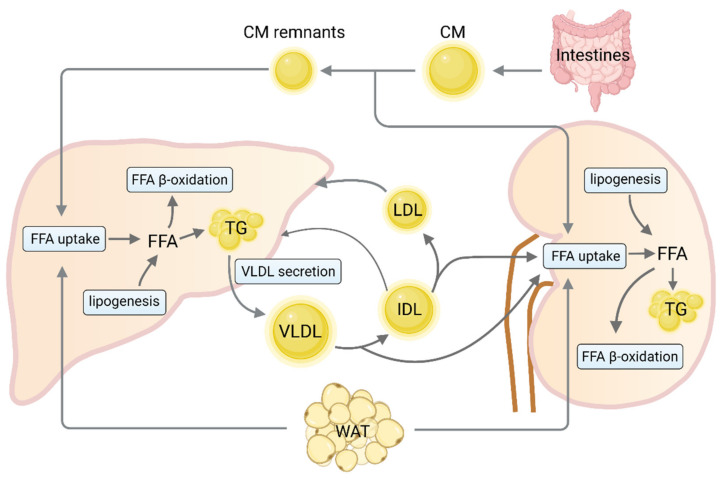
Figure 1.
Cross-talk between liver and kidney in lipid metabolism. Dietary fat is incorporated into CM in the intestine and enters the circulation within two hours after food intake to deliver fatty acids to the kidney before being taken up by the liver as chylomicron remnants. In fasting state, FFA are derived from lipolysis in WAT and are actively taken up by various FA transporters. FFA derived from de novo lipogenesis or circulating are esterified to predominantly produce TG stored within lipid droplets. TG in the liver is packed into VLDL particles and exported into the blood stream for the delivery of fat to the kidney. Alternatively, fatty acids can be oxidized, primarily via β-oxidation, for energy production in the liver and kidney. This figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 2 October 2021). CM, chylomicrons; FFA, free fatty acid; WAT, white adipose tissue; TG, triglycerides; VLDL, very low-density lipoproteins; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein.