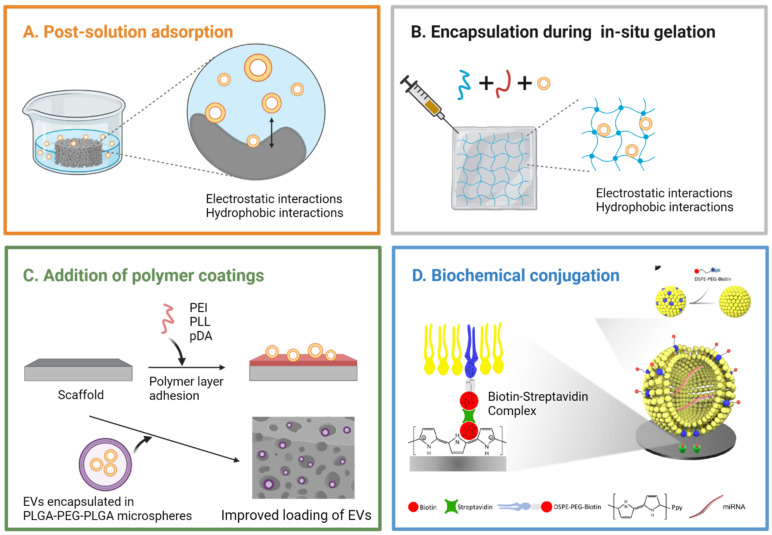
Figure 3.
Schematics of different exosome loading methods to biomaterial scaffolds. (A) In case of post-solution adsorption, scaffolds are incubated in a solution containing exosomes, allowing physical adsorption of exosomes to the surface. (B) Exosomes can be loaded during in situ gelation of hydrogels, in which the pore network of hydrogel plays a critical role in retaining exosomes. (C) Addition of polymer layer onto biomaterial scaffold or encapsulation of exosomes inside polymer microspheres has been applied to advance the integration stability of exosomes to scaffolds. (D) Biotin-streptavidin complex was employed to better immobilize EVs onto the surface of titanium (Ti) scaffolds. The exosomal membrane as well as Ti scaffold surface were chemically modified to enable biotin-streptavidin binding. Panel (D) reproduced with permission of American Chemical Society [65]. Image produced with permission of BioRender.