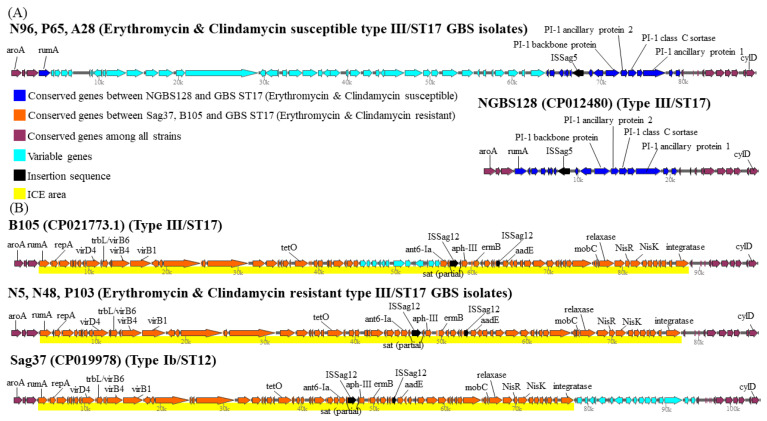
Figure 3.
Pilus Island 1 is a hotspot for integration of integrative and conjugative element, ICESag37, carrying antimicrobial genes and virulence genes. (A) The top schematic shows the region between the beginning of gene aroA and the end of gene cylD (from nucleotides 589,950 to 619,400) in the genome of three antimicrobial susceptible strains (N96, P65, A28) and comparison with that depicted in the second schematic for the region of reference strain NGBS128. This region contains several PI-1 genes (blue) and ISsag5. (B) Loss of PI-1 and ISSag5 is replaced by acquisition of an integrative and conjugative element (ICE), ICESag37, carrying multiple resistance genes and virulence genes in three antimicrobial resistant ST-17/III GBS strains, the reference strain B105 and Sag37 (type Ib/ST12). The bottom schematic show that in these antimicrobial resistant GBS strains, the site-specific integration of ICESag37, starting from the beginning of rumA to the end of integratase, is clearly visible and shown in yellow color. Conserved genes are indicated in purple, variable genes are indicated in light blue. Antimicrobial resistance genes are indicated.