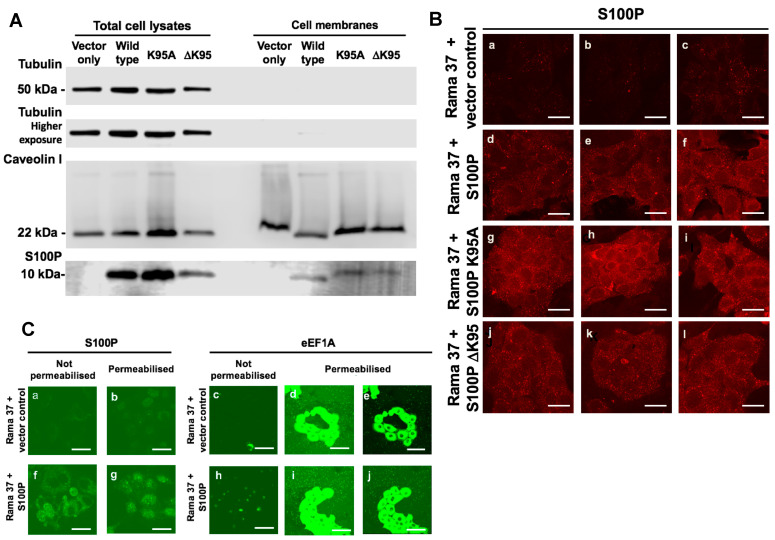
Figure 3.
Association of S100P with cell membranes. (A) Total cell extracts and membrane fractions prepared as described in Materials and Methods from Rama 37 cells expressing S100P proteins and were subjected to Western blotting to detect S100P protein, the cytoplasmic marker, tubulin, and the plasma membrane marker, caveolin 1. (B) Living cells not expressing S100P (Rama 37 + vector control; panels a–c) or expressing wild-type S100P (Rama 37 + S100P; panels d–f), K95A mutant S100P (Rama 37 + S100P K95A; panels g–i), or S100P protein with the C-terminal amino acid deleted (Rama 37 + S100P ΔK95; panels j–l) were incubated with S100P antibody in the culture medium, and bound antibodies were detected with Cy-3-labelled secondary antibody, as described in Materials and Methods and observed with a Zeiss LSM510 confocal laser scanning microscope. Three separate typical fields are shown for each cell line. (C) Antibodies directed at S100P (panels a,f) or cytoplasmic protein, eEF1A (panels c,h), were added to the culture medium of living S100P-negative Rama 37 cells (Rama 37 + vector control; panels a,c) or S100P-positive Rama 37 cells (Rama 37 + S100P; panels f,h). Parallel cultures of S100P-negative cells (Rama 37 + vector control; panels b,d,e) and S100P-positive cells (Rama 37 + S100P; panels g,i,j) were permeabilised before being treated with the antibodies directed at S100P (permeabilised; panels b,g) or eEF1A (permeabilised; panels d,e,i,j). Following fixation, bound antibodies were detected with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibodies (Materials and Methods) and observed with a Zeiss LSM510 confocal laser scanning microscope. Panels (e,j) show the same fields as panels (d,i), but the intensity of the fluorescence signal has been reduced to show individual cells. Bars, (B,C) = 50 μm.