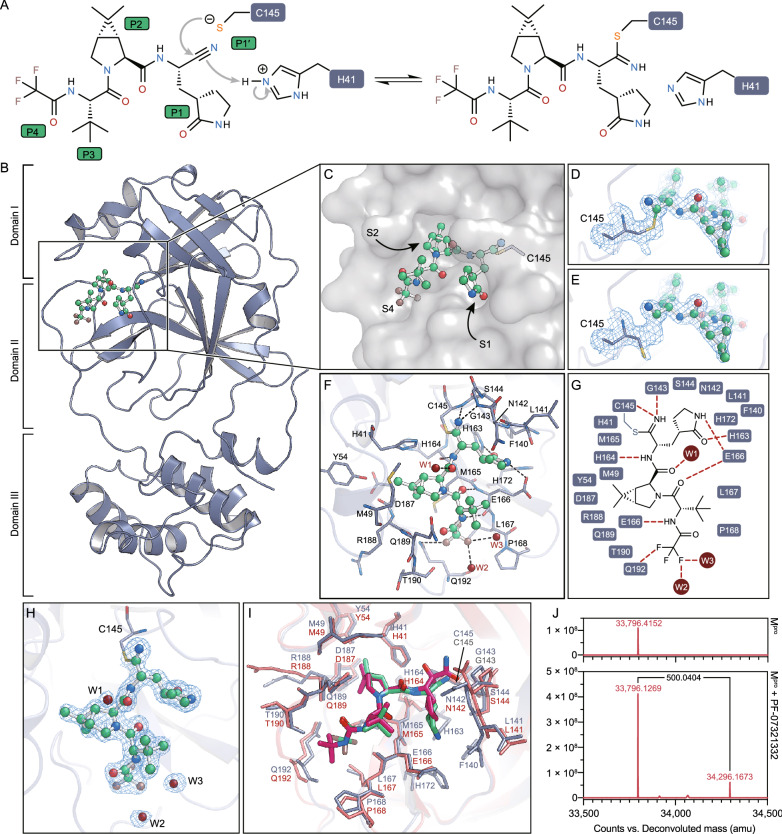
Figure 1.
The structure of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro in complex with PF-07321332. (A) A putative inhibition mechanism of PF-07321332. The catalytic C145 and H41 of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro are highlighted with dark blue squares. P1’, P1, P2 and P4 are highlighted with green squares. (B) The overall structure of a SARS-CoV-2 Mpro protomer. The three domains of Mpro are labeled. The substrate-binding pocket is located within the black box. PF-07321332 is shown as ball-and-stick model with the carbon atoms in bright green, oxygen atoms in bright red, and nitrogen atoms in blue, and fluorine atom in brown. (C) The zoom-in view of the substrate-binding pocket. PF-07321332 forms a covalent bond to C145. Three substrate-binding subsites (S1, S2 and S4) are labeled. (D) The Sγ atom of the catalytic C145 forms a 1.8-Å C-S covalent bond with the nitrile carbon of PF-07321332. The 2Fo-Fc density map contoured at 1.2σ is shown in the light blue mesh. (E) The catalytic C145 in another state where it does not form a covalent bond with PF-07321332. The 2Fo-Fc density map contoured at 1.2σ is shown in the light blue mesh. (F) The detailed binding model in the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-PF07321332 complex structure. The residues that participate in inhibitor binding are shown as sticks. (G) Schematic diagram of the interactions between PF-07321332 and SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. (H) The polder density map of PF-07321332, which is colored as the light blue mesh and contoured at 3.0 σ. (I) The comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-PF07321332 complex structure with that of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-boceprevir. (J) The molecular weights of apo SARS-CoV-2 Mpro and PF-07321332 treated Mpro determined from tandem mass spectrometry. The mass shift (∆m) of the protein is labeled