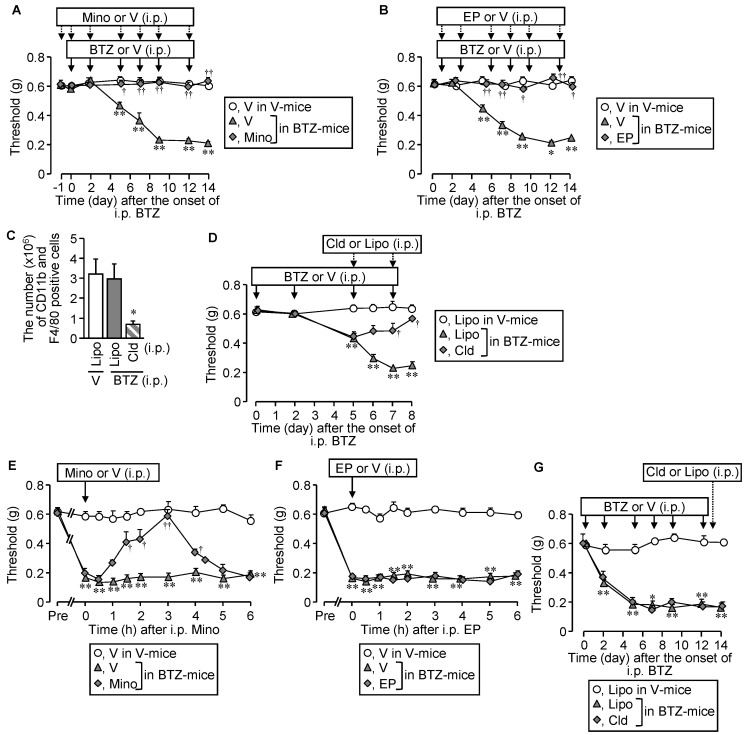
Figure 4.
Effect of macrophage inhibition or depletion on the development of CIPN in mice treated with bortezomib. Bortezomib at 0.4 mg/kg or vehicle was administered i.p. on day 0, 2, 5, 7, 9, and 12. (A,B) Preventive effects of minocycline, a macrophage/microglia inhibitor, and ethyl pyruvate, known to inhibit HMGB1 release from macrophages. Minocycline at 30 mg/kg was administered i.p. once 24 h before the onset of bortezomib treatment and repeatedly 30 min before each dose of bortezomib (A). Ethyl pyruvate at 80 mg/kg was administered i.p. 1 h before each dose of bortezomib (B). (C,D) Effect of macrophage depletion with liposomal clodronate on the development of CIPN caused by bortezomib. The mice received two i.p. administrations of liposomal clodronate at 1.05 mg/mouse or the control liposome on days 5 and 7 after the onset of bortezomib treatment, and successful macrophage depletion in the isolated spleen was confirmed by counting CD11b- and F4/80-positive macrophages in flow cytometry (C). (E–G) Effects of minocycline, ethyl pyruvate, and liposomal clodronate on the established CIPN in mice treated with bortezomib. The mice received a single i.p. administration of minocycline or ethyl pyruvate on day 14 and liposomal clodronate or the control liposome on day 13 after the onset of bortezomib treatment. V, vehicle; BTZ, bortezomib; Mino, minocycline; EP, ethyl pyruvate; Cld, liposomal clodronate; Lipo, control liposome. Data show the mean with S.E.M for 5–6 (A,B,D,E,F), 7–9 (G), or 5 (H) mice. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. V in V-treated mice (A,B,E–G) or Lipo in V-treated mice (C,D,G). † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01 vs. V in BTZ-treated mice (A,B,E) or Lipo in BTZ-treated mice (D).