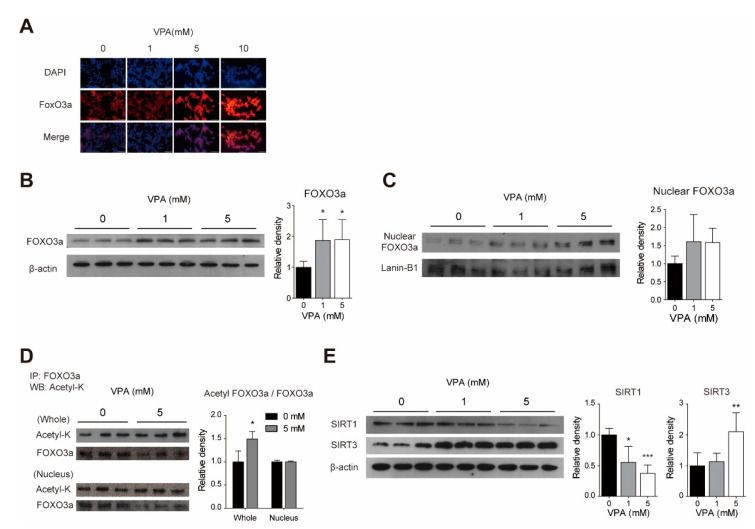
Figure 3.
Acute VPA treatment induced FOXO3a expression in SY-SY5Y cells. VPA modulates the FOXO3a acetylation with the change of SIRT1 and SIRT3 protein levels in SH-SY5Y cells. Expression and location of the target protein were observed in cells treated with different concentrations (0–10 mM) of VPA for 24 h. (A) The location of Foxo3a was observed through immunocytochemistry. 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to confirm nuclear location. Foxo3a was identified as red, and DAPI as blue fluorescence. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Expression of Foxo3a in the total protein extracted with RIPA buffer was confirmed by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C) Nuclear proteins were extracted from the cells using the NEPER kit, and Foxo3a expression was confirmed by Western blot. Lamin-B1 was used as a loading control. (D) The proteins of whole lysate and nucleic fraction were obtained using the IP/Lysis buffer in PierceTMDirect IP Kit and NEPER Kit in SH-SY5Y cells. With these proteins, immunoprecipitation was performed using PierceTMDirect IP Kit and Foxo3a antibody. Expression of acetyl-K was confirmed by Western blot. Foxo3a was used as a loading control. (E) Expression of SIRT1 and SIRT3 in the total protein extracted with RIPA buffer was confirmed by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. The level of protein expression was calculated by analyzing the band with the ImageJ program and normalized against the loading control expression level. Values represent the mean ± SD. (B,C,E) is n = 6 and (D) is n = 3. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 with the 0 mM group.