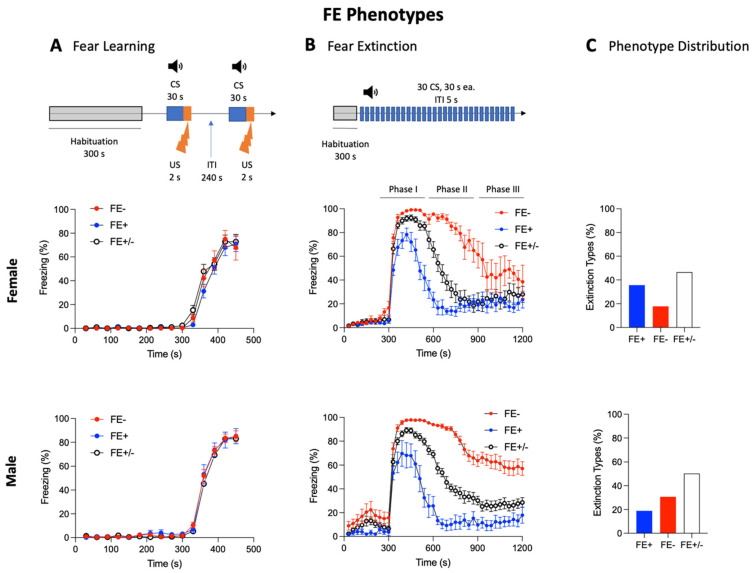
Figure 2.
Inter-individual and sex differences in fear extinction learning ability in naïve female and male rats. Fear conditioning on Day 1 (A) and extinction (B) tests were conducted using two distinct context chambers. (A) Fear conditioning on Day 1—rats were habituated to context A followed by fear conditioning (2 CS-US pairs, see Section 2.5.1). The diagram illustrates the experimental protocol. Symbols in the line graph show freezing responses expressed in percent per 30 s segment during fear conditioning with 2 CS-US pairings. (B) Fear extinction learning on Day 2—rats were habituated to context B followed by extinction training (30 CSs, no US). The diagram illustrates the experimental protocol. Symbols in the line graph show freezing responses to tone (CS) expressed in percent per 30 s segment. (C) Bar histograms show the distribution of rats with strong (FE+), “normal” (FE+/−), and weak (FE−) fear extinction. The population (%) of FE+ was larger in female rats compared to male rats. For details, see the “Methods” and “Results” sections. CS: conditioned stimulus; US: unconditioned stimulus; ITI: intertone interval; FE: fear extinction.