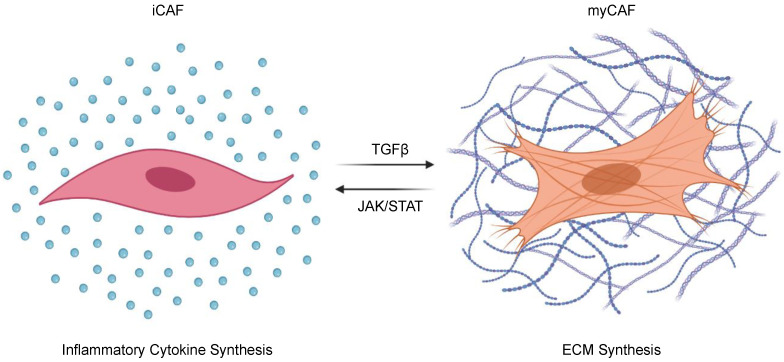
Figure 2.
The effects of TGFβ signals on cancer-associated fibroblast polarization. Cancer-associated-fibroblasts (CAFs) can be sub-categorized into inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs) that enhance local inflammatory cues through the secretion of cytokines such as interleukin 6 (IL-6) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF); and myofibroblastic CAFs (myCAFs) that hyper-secrete extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. The balance between iCAFs and myCAFs is determined by competition between TGFβ and JAK/STAT signaling pathways, where TGFβ signaling polarizes CAFs toward a pro-fibrotic myCAF phenotype.